Fig. 1.
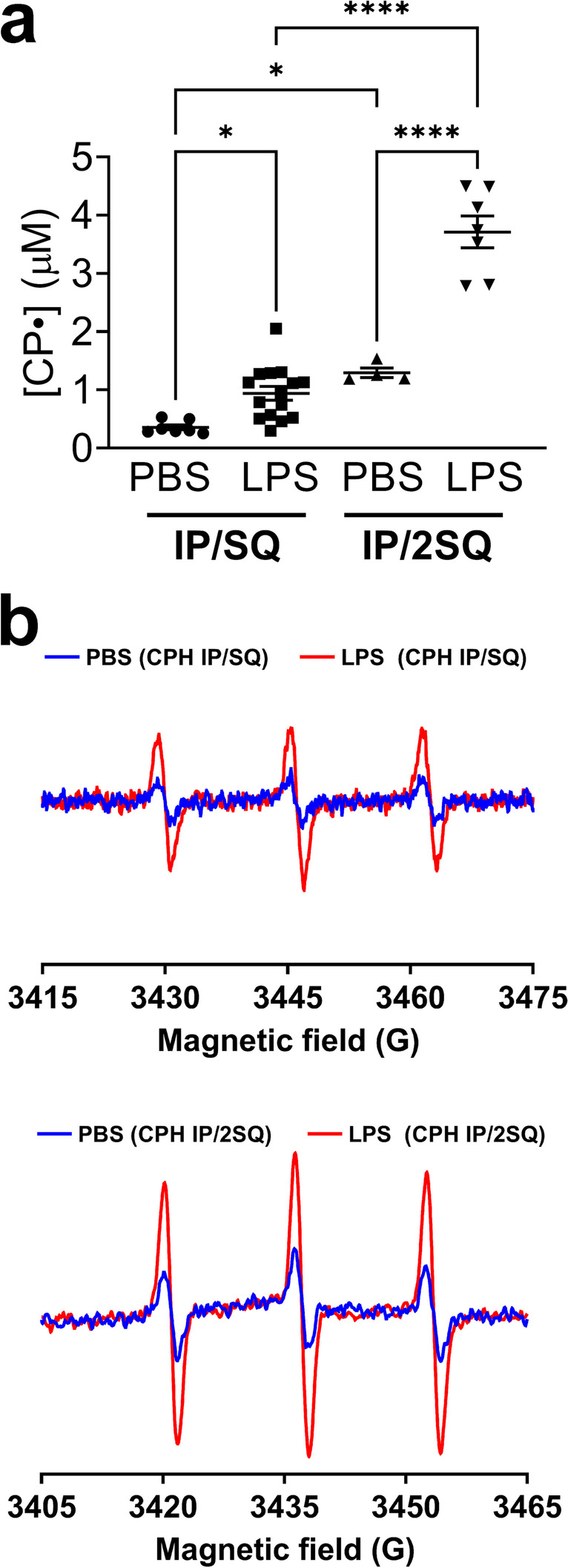
Optimization of spin probe delivery method to detect cellular superoxide in the lung of LPS-treated and control mice. Mice were treated with LPS (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneal (IP) injection). After 24 h mice were injected with CPH with two dosing strategies: 1) Concurrent IP and subcutaneous (SQ) injection, followed by lung harvest 1 h later (protocol IP/SQ); 2) Concurrent IP and SQ injection plus a second SQ injection 30 min later, with lung harvest after a further 30 min (protocol IP/2SQ). See Materials and Methods for details. (a) Concentration of nitroxide CP• in the lungs of PBS- and LPS-treated mice. (b) EPR spectra of nitroxide CP• in the lungs of mice that were PBS-treated (blue traces) and LPS-treated (red traces) following the two dosing strategies. Measurements at X-band were done at room temperature. Data expressed as mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001 (n = 4–15)
