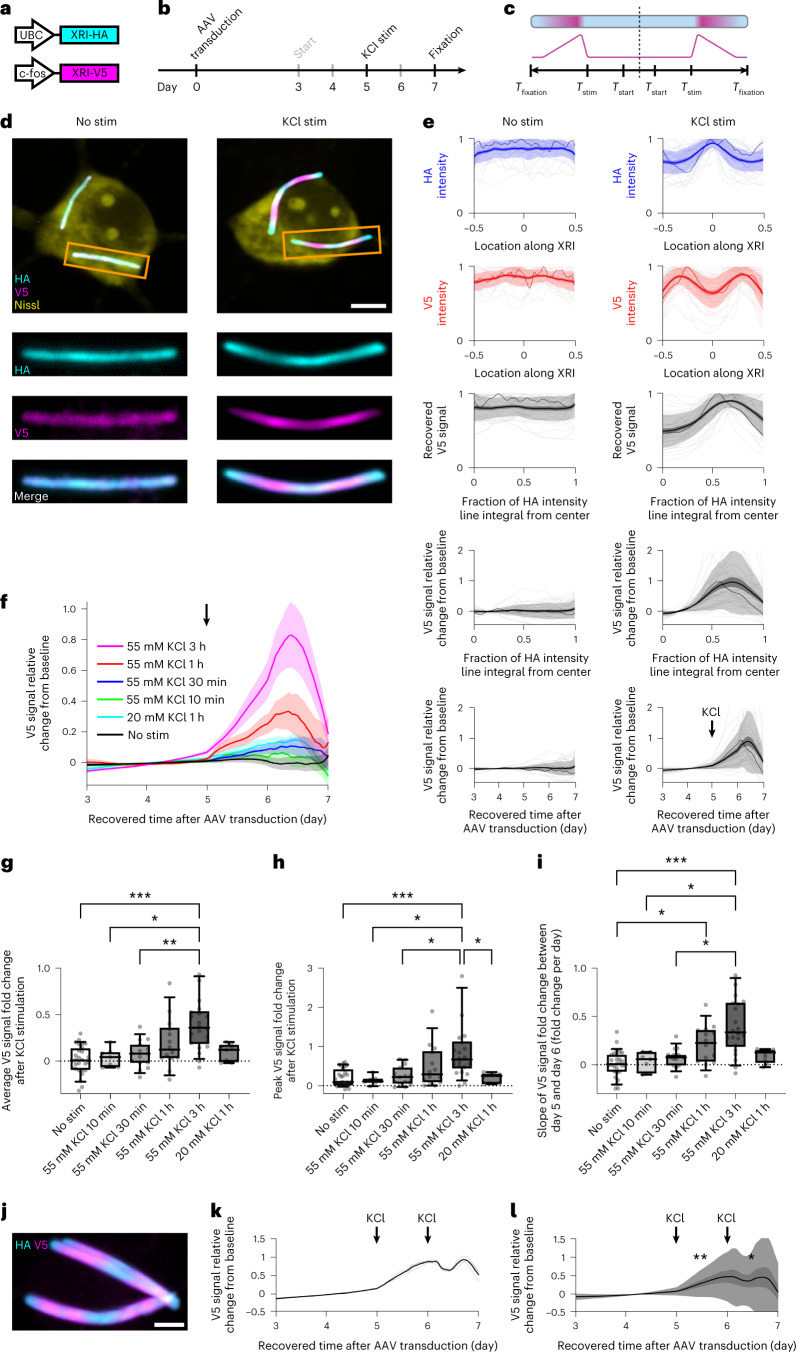
Fig. 3. Recording the timecourse of c-fos-promoter-driven expression with XRI.
a–c, Schematics of the AAV constructs cotransduced to neurons (a), experiment pipeline (b) and expected epitope distribution along the XRI protein self-assembly (c) in the c-fos-promoter-driven gene expression experiment. XRI-HA, XRI with the epitope tag HA; XRI-V5, XRI with the epitope tag V5; c-fos, c-fos promoter; Tstim, the time of the onset of stimulation of neuron activity by KCl; Tstart, the time at which XRI starts recording information after gene delivery and expression of XRI, which is measured to be 3 days after AAV transduction in Fig. 2f. d, Representative confocal images of cultured mouse hippocampal neurons expressing constructs in a, taken after fixation, Nissl staining and immunostaining against HA and V5 tags. KCl stim, 55 mM KCl stimulation for 3 h starting at Tstim = 5 days; three rows of rectangular panels at the bottom, enlarged views of regions marked in orange rectangles in the top row of square panels. Scale bar, 5 µm. e, HA intensity profile along the XRI (first row), V5 intensity profile along the XRI (second row), recovered V5 signal (calculated from the intensity profiles) plotted against the fraction of the line integral of HA intensity (third row), V5 signal relative change from baseline (ratio of the V5 signal to the V5 signal at the center of the XRI, and then minus 1) plotted against the fraction of the line integral of HA intensity (fourth row) and V5 signal relative change from baseline plotted against recovered time after AAV transduction (using the black line in Fig. 2h as time calibration for time recovery from the line integral of HA intensity; fifth row), from the experiment described in a–c (n = 30 XRIs from 28 neurons from two cultures for ‘No Stim’ group; n = 40 XRIs from 22 neurons from three cultures for ‘KCl Stim’ group). Thick centerline, mean; darker boundary in the close vicinity of the thick centerline, s.e.m.; lighter boundary, s.d.; lighter thin lines, data from individual XRIs; darker thin line, data from the corresponding XRI in the orange rectangle in d. In the first three rows, each raw trace was normalized to its peak to show relative changes before averaging. See Extended Data Fig. 5 for the detailed process flow of extracting signals from XRI assemblies. f, V5 signal relative change from baseline plotted against recovered time after AAV transduction from XRIs in neurons under different KCl stimulations at Tstim = 5 days (black arrow, onset of KCl stimulation; n = 22 neurons from three cultures for ‘55 mM KCl 3 h’ group; n = 14 neurons from four cultures for ‘55 mM KCl 1 h’ group; n = 15 neurons from two cultures for ‘55 mM KCl 30 min’ group; n = 7 neurons from one culture for ‘55 mM KCl 10 min’ group; n = 9 neurons from one culture for ‘20 mM KCl 1 h’ group; n = 28 neurons from two cultures for ‘No Stim’ group;). Centerline, mean; shaded boundary, standard error of mean. g–i, Box plot of the average V5 signal relative change from baseline over time between day 5 and day 7 (that is, within 48 h after the onset time of KCl stimulation) (g), the peak V5 signal relative change from baseline over time between day 5 and day 7 (h) and the slope of V5 signal relative change over time from baseline between day 5 and day 6 (i) for neurons in f. Middle line in box plot, median; box boundary, interquartile range; whiskers, 10–90 percentile; minimum and maximum, not indicated in the box plot; gray dots, individual datapoints. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; Kruskal–Wallis analysis of variance followed by post hoc Dunnʼs tests between every two groups; test result was not significant for a pair without *, ** or *** indicated. j, A representative confocal image of XRIs in a cultured mouse hippocampal neuron expressing constructs in a, taken after fixation (7 days after AAV transduction), Nissl staining and immunostaining against HA and V5 tags. Neurons were stimulated twice, first at Tstim = 5 days and then at Tstim = 6 days, each time by 55 mM KCl for 1 h. Scale bar, 5 µm. k, V5 signal relative change from baseline plotted against recovered time after AAV transduction for the XRIs shown in j. Thin lines, traces from individual XRIs; thick line, the averaged trace over all XRIs. l, V5 signal relative change from baseline plotted against recovered time after AAV transduction for XRIs in neurons under two sequential KCl stimulations as described in j (n = 16 neurons from two cultures). Thick centerline, mean; darker boundary in the close vicinity of the thick centerline, s.e.m.; lighter boundary, s.d. *P = 0.0118; **P = 0.0097; Kruskal–Wallis analysis of variance followed by post hoc Dunnʼs tests between the peak V5 signal relative change during T = 5–6 (or 6–7) days after AAV transduction and the baseline V5 signal relative change (that is, the V5 signal relative change averaged over T = 3–5 days after AAV transduction). See Supplementary Table 3 for details of statistical analysis.