Figure 1.
sEV-derived CC16 is reduced in BALF from pneumonia patients
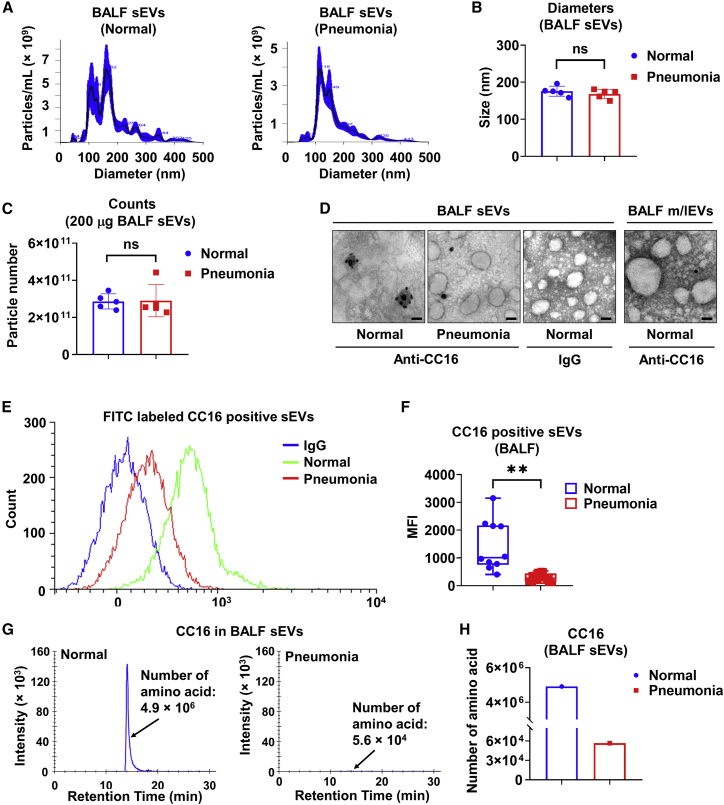
(A–D) Two-hundred micrograms of BALF sEVs from pooled normal human (n = 10) and pneumonia patients (n = 21) are randomly pooled as five pairs per group. sEVs samples are examined by NTA to analyze size distribution (A), average size (B), and particle numbers (C). Data are mean ± SD. Ns, not significant, p > 0.05. (D) Representative TEM images of BALF-derived sEVs are shown. sEV samples were stained using immunogold labeling with the antibody against CC16. Scale bar, 100 nm. (E and F) Detection of CC16-positive BALF sEVs from healthy (n = 10) and pneumonia patients (n = 21) using flow cytometry (E). Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) is measured (F). The boxes in the boxplots show the medians with 25th and 75th percentiles, and the whiskers show the minimum and maximum values. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus the normal group. (G and H) Pooled BALF sEVs from normal human (n = 10) and pneumonia patients (n = 21) were purified. Twenty micrograms of pooled sEVs from each group are used for measuring the amino acid number of CC16 by MS.