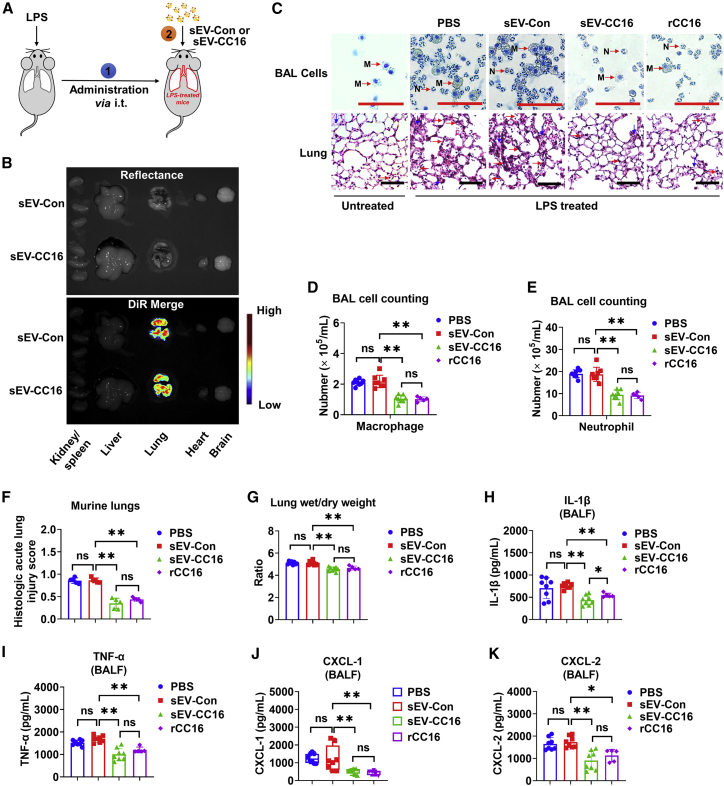
Figure 3.
sEV-CC16 protects against LPS-induced lung injury in mice
Three hours after LPS, mice (five to eight mice per group) were given PBS, sEV-Con, sEV-CC16, or rCC16 and sacrificed 24 h after the indicated treatments. Schematic illustration of delivery of sEV-Con and sEV-CC16 into LPS-pretreated mice (A). In vivo imaging systems (IVIS) images of major organs obtained 24 h after the delivery of DiR-labeled sEVs (B). H&E staining of BAL cells and lung sections. M, macrophage; N, neutrophil; red arrows, neutrophils; blue arrows, alveolar disruption with hyaline membranes. Scale bar, 100 μm (C). The number of BALF macrophages (D) or neutrophils (E). Lung injury scored (F). Lung wet-to-dry weight ratios (G). Protein levels of IL-1β (H), TNF-α (I), CXCL-1 (J), and CXCL-2 (K) in BALF detected using ELISAs. The results presented as mean ± SD. In (D)–(I) and (K), the data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD. In (J), the boxes in the boxplots show the medians with 25th and 75th percentiles, and the whiskers show the minimum and maximum values. Data are analyzed by the Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis followed by pairwise comparisons using Mann-Whitney U tests. ns, p > 0.05; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01.