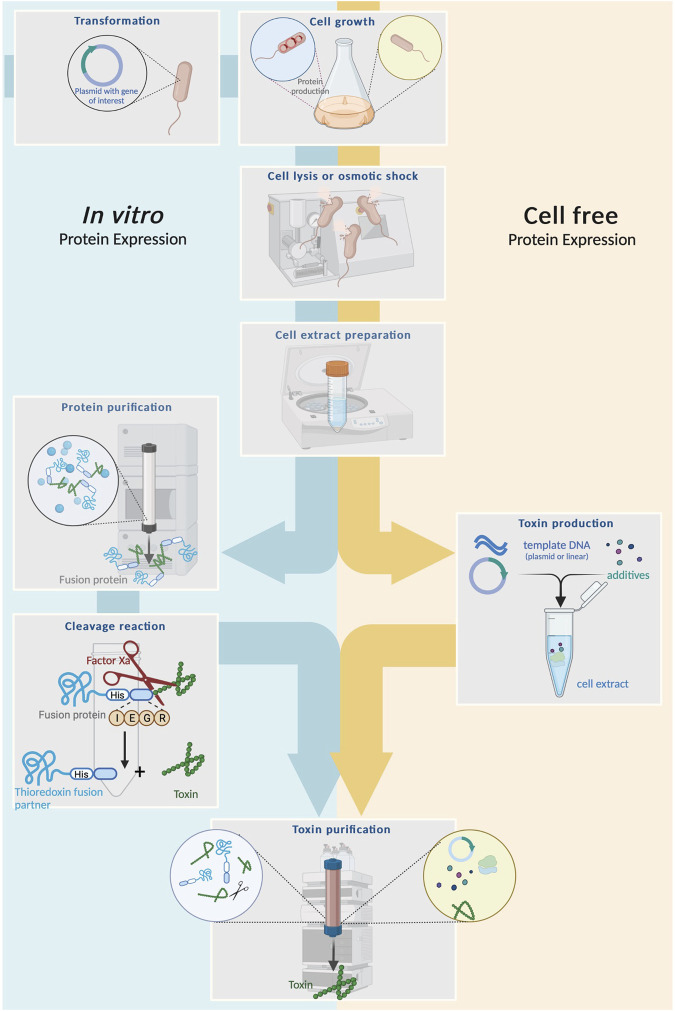
FIGURE 4.
Schematic comparison between heterologous expression and cell-free system for venom toxin production. Left: Heterologous expression begins with cloning of plasmids carrying a gene for the toxin of interest and a fusion partner into a suitable host cell followed by cultivation, lysis and purification of the fusion protein. The latter is subsequentially cleaved with (e.g., by factor Xa) to release the mature toxin. Finally, the toxin is purified via chromatography. Right: Cell-free systems usually start from intact host cells, which are cultivated and lysed to create a cell extract, serving as the primary expression medium. Template DNA encoding the toxin of interest (either a linear gene fragment or a plasmid) plus additives are added and protein synthesis is facilited by the cell lysate. From here, produced toxin can be isolated from the extracted via chromatography.