Figure 2.
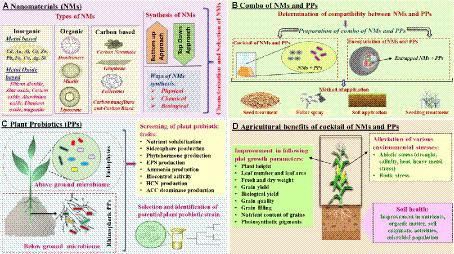
(A) Representation of NMs categorized into the following: inorganic-based (metal-based and metal oxide-based), organic NMs (dendrimers, micells, and liposomes), carbon-based NMs (carbon nanotubes, graphene, fullerenes, carbon nanofibers, and carbon black), and their approaches of synthesis (bottom-up and top-down) with their three physical, chemical, and biological ways of synthesis. (B) The schematization of PPs, especially endophytes and rhizospheric PPs, and their screening on various traits such as nutrient solubilization, production of siderophore, phytohormone, EPS, ammonia, HCN, ACC deaminase, and biocontrol activity. (C) Determination of compatibility between NMs and PPs, and preparation of their combo, either a cocktail of NMs and PPs or the encapsulation of NMs and PPs. Such a combo can be applied by following suitable methods such as seed treatment, foliar spraying, soil application, and seedling treatment. (D) Illustration of the agricultural benefits resulting from the application of a cocktail of NMs and PPs in terms of improvement in plant growth parameters, alleviation of environmental stresses, and prolific effects on soil health.
