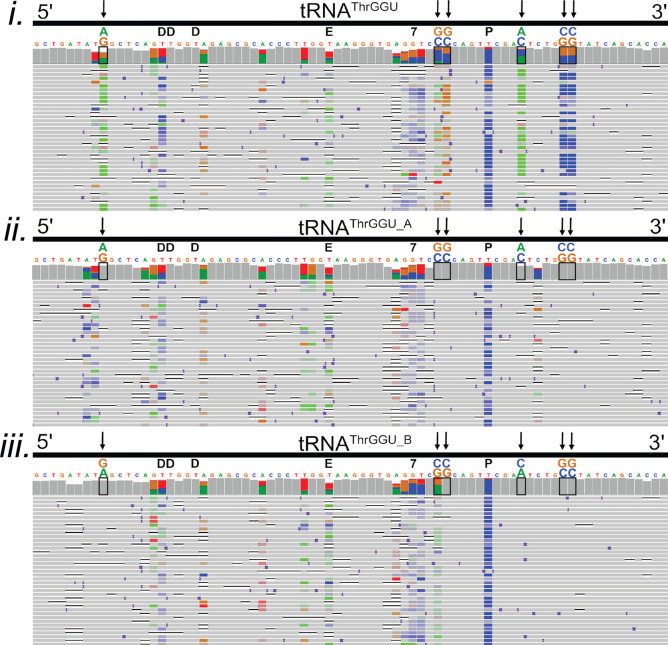
Figure 5.
Confirmation of two known isodecoders in nanopore tRNAThrGGU sequence alignments. The isoacceptor tRNAThrGGU has two isodecoder forms which have canonical sequence variations at positions 9 (G/A), 49 (C/G), 50 (C/G), 59 (C/A), 64 (G/C), and 65 (G/C).3 (i–iii) Black boxes on the IGV coverage plots surround the positions of these variations. Black arrows also point to variant positions for clarity. Above each black box, the reference nucleotide is enlarged, and the alternative nucleotide is above it, labeled and colored in accordance with IGV schema (A = green, G = gold, C = blue, and T(U) = red). (i) Alignments of total E. coli tRNA reads to the tRNAThrGGU isoacceptor. At positions that vary between tRNAThrGGU isodecoders, the colors representing the reference and alternative nucleotides are seen in the coverage plot. This can be interpreted as both isodecoder forms being present in the data. (ii) Alignments of total E. coli tRNA read to the tRNAThrGGU_A isodecoder. Gray in the coverage plot and the rows of aligned reads indicate agreement with the tRNAThrGGU_A reference. (iii) Alignments of total E. coli tRNA read to the tRNAThrGGU_B isodecoder. Gray in the coverage plot and the rows of aligned reads indicate agreement with the tRNAThrGGU_B reference. The known modifications D (dihydrouridine), E (N6-methyl-N6-threonylcarbomoyladenosine), 7 (7-methylguanosine), and P (pseudouridine) are denoted in black above the reference sequence.3 Adapter sequences were included in the alignments but are not shown.