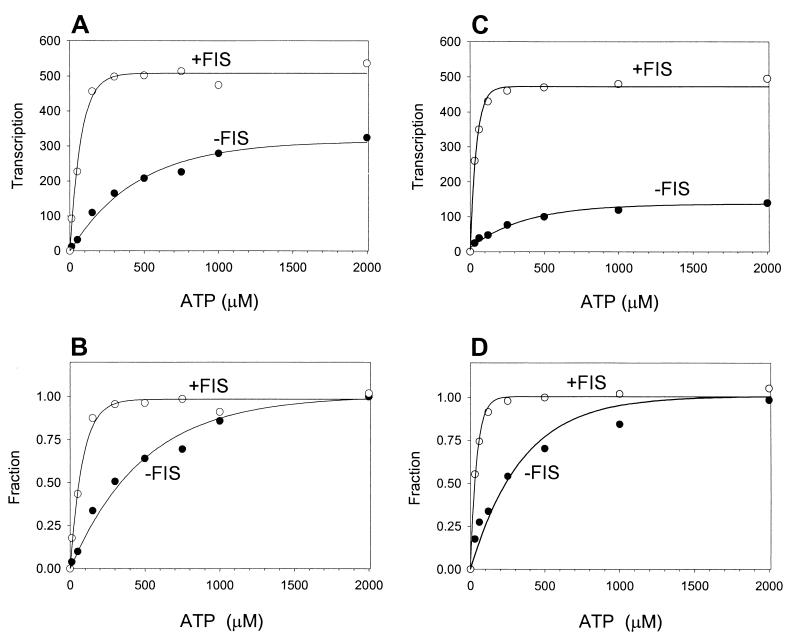
FIG. 3.
Effect of FIS on initiating NTP levels required for rrnB P1 transcription. (A) Transcription by the β′ Δ215–220 mutant RNAP at different ATP concentrations. In vitro transcription was performed as described in Materials and Methods with 100 mM NaCl, using supercoiled plasmid templates containing the rrnB P1 (−154 to +50) promoter in the absence or presence of FIS. (B) Results from panel A normalized to those obtained with 2 mM ATP. The graphed data represent averages from two experiments. The apparent KATPs in the absence and presence of FIS are about 330 and 60 μM, respectively. (C) Transcription by the wild-type RNAP at different ATP concentrations. In vitro transcription was performed as described in Materials and Methods with 130 mM NaCl, using supercoiled plasmid templates containing the rrnB P1 (−154 to +50) promoter in the absence or presence of FIS. (D) Results from panel A normalized to those obtained with 2 mM ATP. The graphed data represent averages from two experiments. The apparent KATPs in the absence and presence of FIS are about 240 and 30 μM, respectively.