Fig. (2).
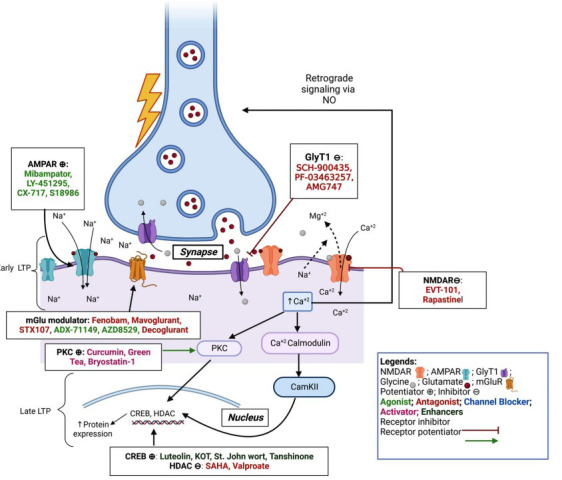
Excitotoxic pathway and drugs acting on it: NMDA, AMPA, and mGlu receptors are involved in the excitotoxicity process in cells. The early phase LTP is modulated by AMPAR (blue) action activated by Glut released from presynaptic vesicles, causing its activation and import of sodium ions, leading to depolarization. The depolarized membrane potential and Glut (red) and Gly (grey) together allow activation of NMDAR (pink) by binding to their respective binding sites on NMDAR, allowing Ca2+ ions influx. The mGluR (yellow) allows the influx of Ca2+ ions in a cell at the late phases of LTP, leading to stronger signaling in the cell. The Ca2+ ions activate Ca2+/Calmodulin protein activating protein kinase (PKC, CaKII), leading to increased mRNA and protein expression like CREB, HDAC, etc. The Ca2+ ions also activate the NOS leading to NO production and retrograde signaling and releasing Glut from presynaptic sites. The entire cycle helps in the formation of neuroprotective protein expression.
