Table 1.
Phytoestrogens conferring neuroprotection against radiation-induced neuronal injury in vivo and in vitro.
| Compound | Structure | Treatment (Dose and Duration) | Experimental Model | Radiation (Type, Dose) |
Major
Outcomes |
Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin |
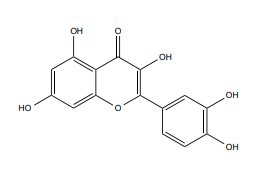
|
50 mg/kg | Male Wistar-Albino rats, 300–350 g | 20 Gy | ↑ Neuroprotection ↑ Antioxidant activity |
↑Regulate plasma MDA, TAS | [234] |
| 5-100 μM, 24 hrs | Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons | γ-ray, 2 Gy | ↓ Inflammatory responses, ER stress, | ↓ BiP and C/EBP ↓ TNF-α, JNK ↑Tuj1, BDNF |
[235] | ||
| Chrysin |
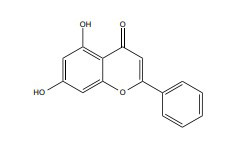
|
- | Male albino rats, 140-160 g | 5 Gy | ↓Oxidative damage | ↑ GSH,BDNF ↓MDA, TNF-Α, GABA |
[237] |
| 50 mg/kg 21days |
Male Wister rats, 120–150 g | γ-ray,5 Gy | ↓Oxidative damage | ↑Catecholamine content’ creatinine kinase-BB ↓ MDA, β-amyloid, acetylcholinesterase and caspase-3 |
[236] | ||
| Curcumin |
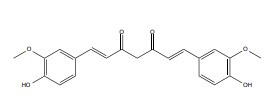
|
200 mg/kg | Kunming mice, 6–7 weeks | Heavy-ion radiation, 4 Gy. | ↑ Cognitive functions | ↑SOD, MDA ↓ NAD(P)H, NQO1, HO-1, γ-GCS |
[240] |
| 150 mg/kg, 7 days | - | γ-ray, 15 Gy |
↓ Heart injury | ↑IL-4 ↓ Duox1 and Duox2 |
[246] | ||
| Flaxseed oil | -- | 100 µl/mice/day (21days) |
Swiss albino 6-8 weeks, 25±2 gm | 7 Gy | ↓ Oxidative damage | ↓ Lipid peroxidation (LPO), ↑ Glutathione (GSH) |
[238] |
| Resveratrol |
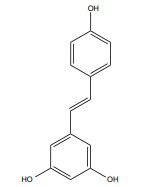
|
5 -10 mg/kg, 21 days |
Male Sprague Dawley rats, 200-220 g |
γ-ray, 4-Gy |
↑ Apoptosis ↑ Oxidative damage |
↑ Sirt1 mRNA ↑ ROS-scavenging |
[242] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) |
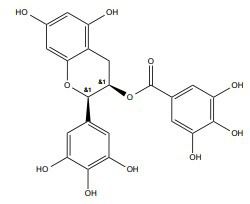
|
2.5-5 mg/kg/d | Male Wister rats | γ-ray, 4 Gy |
↓DNA damage and apoptosis | ↓ Homocysteine, ↓ Amyloid β, TNF-α, IL-6 levels ↑ Dopamine and serotonin ↓ Cytochrome-c, Bax, and caspase-3 and 9 ↑ Bcl-2 |
[243] |
| Silymarin |
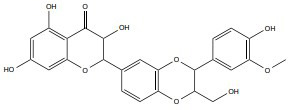
|
140 mg/kg/d | Rat model | γ-ray, 0.2-0.6 Gy |
↑ Repair DNA damage | ↑Nucleic acids, histone proteins stability ↓Free radical generation ↓Lipid peroxidation |
[244] |
| Baicalein |
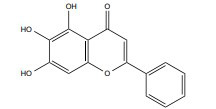
|
10 mg/kg/d | C57BL/6 mice | γ-ray, 5 Gy |
↑ Neurogenesis regulation | ↑BDNF-pCREB | [245] |
