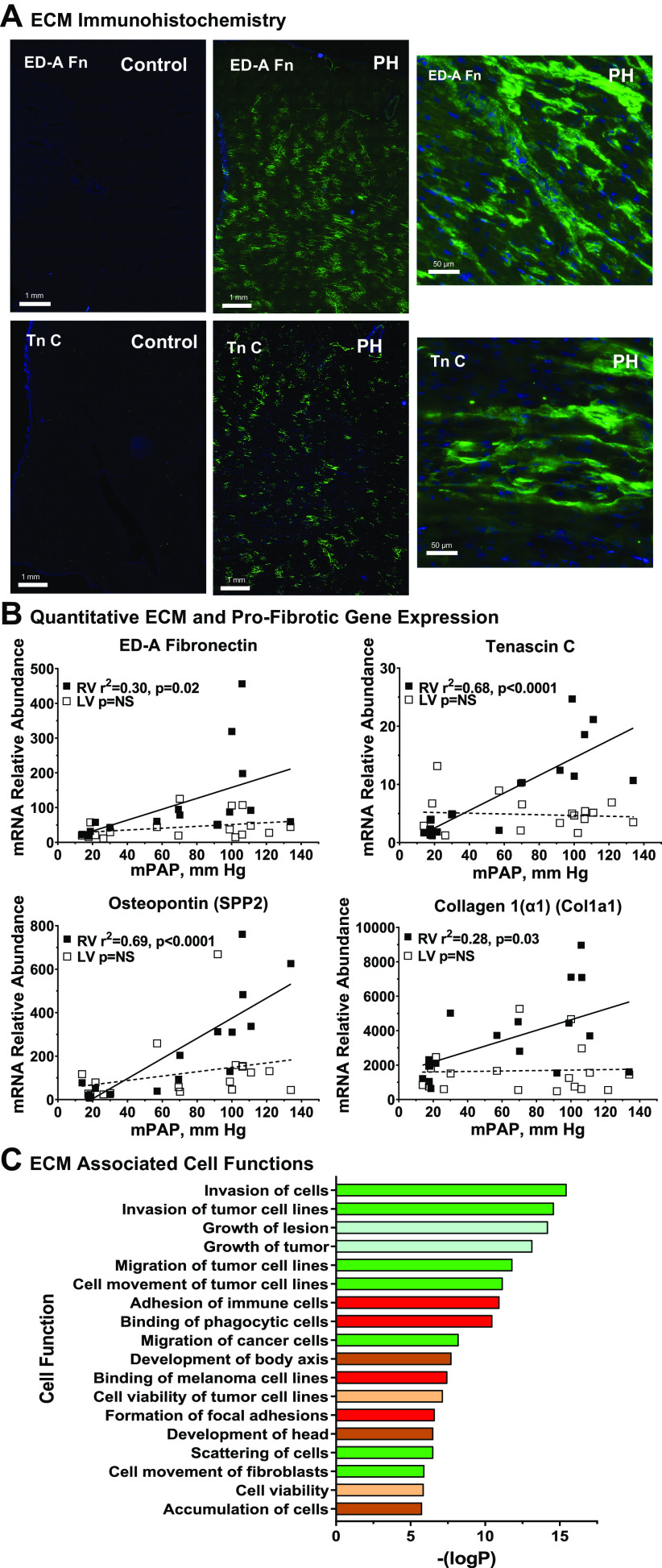
Figure 5.
Molecular and cellular correlates of right ventricular (RV) extracellular matrix remodeling in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH). A: extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling in hypertensive calf RV. Cryosections of RV free wall were collected from PH and control calves and stained for extracellular domain-A (ED-A) fibronectin, or tenascin C as described in materials and methods. Representative images from PH and control animals (n = 4 each) are shown with wide field and higher resolution views, scale as indicated. B: quantitative PCR evaluation of ECM gene expression. Abundances of the indicated mRNAs were determined by real-time PCR from RV or left ventricular (LV) tissues of control and PH calves. The relationship of mRNA abundance to mean pulmonary artery pressure was determined by linear regression. Black square, RV; white square, LV. C: functional responses associated with ECM and profibrotic genes. Genes associated with the terms cardiovascular “ECM” or “fibrosis” were identified and their functional associations with gene-ontological categories were determined with Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Functional subcategories are listed according to –log (enrichment P value), all z-scores > 2.0. Major functional categories are indicated by color: green square, cell movement; red square, cell-cell interaction; blue square, organ injury and abnormality; brown square, embryonic and organismal development; tan square, cell death and survival.