FIGURE 5.
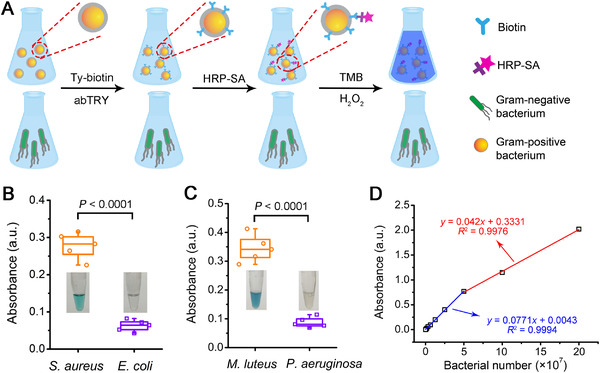
Naked‐eye detection of Gram‐positive bacteria. (A) Scheme illustrating the experimental procedures for naked‐eye differentiation of Gram‐positive bacteria from Gram‐negative bacteria. (B) Absorbance of the “TMB + H2O2” solutions after being added with S. aureus or E. coli bacteria that were first treated with Ty‐biotin (10 µg mL−1) and abTYR (0.17 µM) and then incubated with SA‐HRP (20 µg mL−1), followed by PBS washing for three times. Inset: representative photographs of the “TMB + H2O2” solutions added with S. aureus (left) or E. coli (right) bacteria receiving the abovementioned treatments. Statistical significance between the indicated groups was calculated using two‐sided unpaired t‐test. (C) Absorbance of the “TMB + H2O2” solutions after being added with M. luteus or P. aeruginosa bacteria subjected to the treatments described in (B). Inset: representative photographs of the “TMB + H2O2” solutions added with M. luteus (left) or P. aeruginosa (right) bacteria treated as mentioned above. Statistical significance between the indicated groups was calculated using two‐sided unpaired t‐test. (D) Plot of the absorbance of “TMB + H2O2” solutions versus the number of HRP‐labeled S. aureus bacteria that were added to the sensing system
