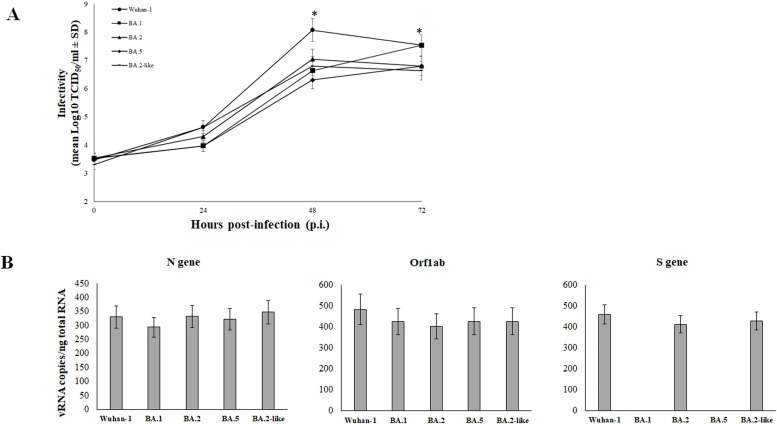
Fig. 3.
The Wuhan-1 SARS-CoV-2 variant outcompeted the replication of Omicron variants. (A) Calu-3 cells were infected by Wuhan-1 and Omicron BA.1, BA.2, BA.5 and BA.2-like variants at a MOI of 0.01. Cell culture supernatants were collected at 24h, 48h and 72h post-infection (p.i.) and viable released virus content was assessed by microtitration assay. Results were presented as mean viral titer expressed as tissue culture dose 50 (TCID50)/ml ± standard deviations (SD) from three separate experiments. Significance was determined using unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test as p<0.05, *. (B) Intracellular viral copy numbers (Cp) of N, S and Orf1ab genes was assessed by RT-qPCR on Calu-3 cells infected at MOI=0.01 with Wuhan-1 and Omicron BA.1, BA.2, BA.5 and BA.2-like variants, collected at 72h p.i. The S gene target detection was impacted by the presence of a six-nucleotide deletion corresponding to the amino-acid 69-70 (D69-70) present in the BA.1 and BA.5 Omicron sub-lineages, rather than to the lack of gene expression. Results were presented as mean Cp/ng of input purified total RNA ± standard deviations (SD) from three separate experiments. Significance was determined using unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test as p>0.05, n.s.