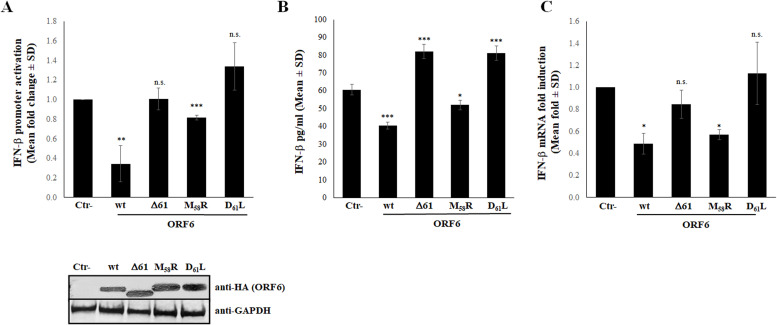
Fig. 4.
Inhibitory activity of SARS-COV-2 ORF6 protein variants. (A) HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with the IFN-β promoter-mediated firefly luciferase (pIFN-β) reporter plasmid in combination with wild-type, Δ61 and the D61L or M58R ORF6 inactive mutant expressing plasmids or with empty vector (Ctr-). At 36h post-transfection, cells were poly(I:C)-stimulated by transfection. Firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were evaluated at 48h post-transfection. Three (n=3) independent experiments were performed. Representative data are presented as mean fold change of relative luminescence unit (RLU) ± standard deviations (SD). (B) The production of IFN-β was tested by enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) in supernatant of wild-type, M58R, D61L or Δ61 ORF6 expressing A549 cells. Negative control (Ctr-) was represented by A549 cells transfected with empty plasmid alone. Quantitative evaluation, based on relative standard curves, was performed. Results are reported as mean concentration (pg/ml) ± standard deviations (SD) from at least three separate experiments (n>3). (C) IFN-β expression was evaluated in A549 cells expressing different ORF6 mutants by specific IFN-β mRNA quantification using quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Ribonuclease P (RNaseP) gene expression was used for relative quantification based on 2-ΔΔCt method. With respect to Wuhan-1 reference strain, significance was determined using unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test as p<0.0005, ⁎⁎⁎; p<0.005, ⁎⁎; p<0.05, *; p>0.05, n.s.