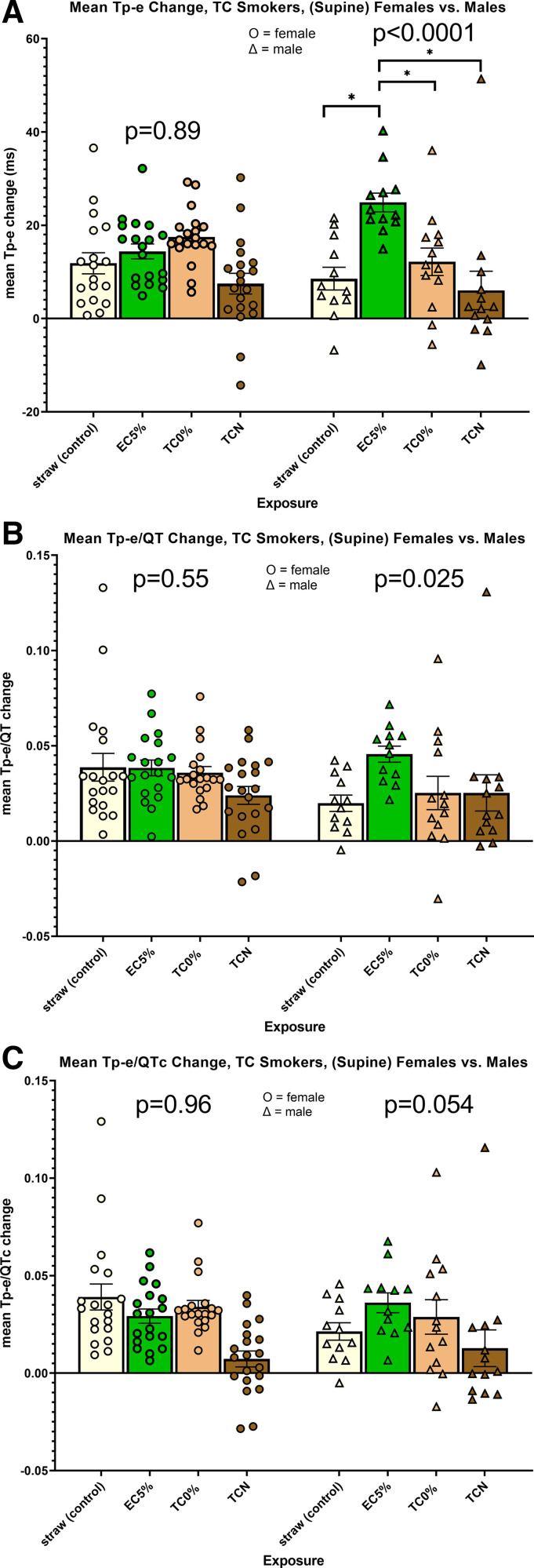
Figure 3.
Changes in ECG indices of ventricular repolarization following acute exposures within the tobacco cigarette cohort segregated by sex. A: interaction term between exposure and sex for the primary outcome of Tpeak-Tend (Tp-e) was highly significant (P = 0.0008). When analyzed by sex, the overall P value among the four exposures in males (P < 0.0001) but not females (P = 0.89) was highly significant. In males only, prolongation of the Tp-e interval after using the electronic cigarette with nicotine was significantly greater compared with all other exposures. B: interaction term between exposure and sex for the primary outcome of Tp-e/QT was statistically significant (P = 0.039), and the overall P value among exposures in males was significant (P = 0.025), but not in females (P = 0.55). None of the pairwise individual comparisons among exposures reached statistical significance. C: interaction term between exposure and sex for the primary outcome of Tp-e/QTc trended toward significance (P = 0.067), as did the overall P value among exposures in males (P = 0.054), but not females (P = 0.96); t test, *P < 0.0001. EC5%, electronic cigarette with 5% nicotine; TC, tobacco cigarette; TC0%, tobacco cigarette (research) with minimal nicotine; TCN, commercial tobacco cigarette with nicotine.