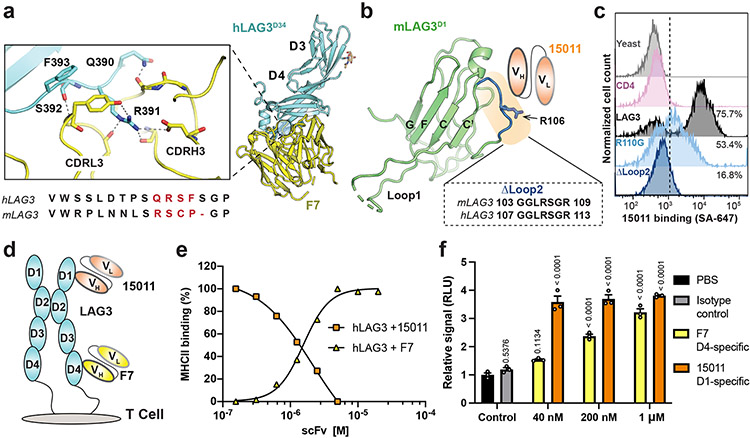
Figure 3. Epitope mapping and functional characterization of LAG3 antagonist scFvs.
a, Zoom window depicting F7 epitope on the hLAG3D34:F7 structure. The F7-bound residues in hLAG3 (depicted below the zoom panel) are not conserved in mLAG3. b, The Arg106 residue and Loop 2 epitope recognized by 15011 are highlighted on the structure of the mLAG3 D1 domain. A sequence alignment shows the conservation of mLAG3 and hLAG3 Loop 2 residues. c, Flow cytometry histogram plots depicting the binding of yeast-displayed CD4, hLAG3, hLAG3R110G, and hLAG3ΔLoop2 to 15011. d, Cartoon representations of F7 and 15011 scFvs binding to hLAG3. e, An SPR-based competition assay was performed to determine whether the 15011 or F7 inhibits hLAG3:MHCII interactions. Fixed concentrations of hLAG3 (800 nM) mixed with various concentrations of 15011-Fc or F7-Fc fusion proteins were injected over a sensor chip coated with HLA-DR4. ΔRU was calculated by subtracting the Rmax of hLAG3 alone from the Rmax of hLAG3:scFv complexes. The curves were plotted from 1 of 2 representative experiments. f, NFAT reporter assay comparing potency of F7 and 15011 as LAG3 antagonists. Net signals were normalized to a PBS control for analyzing RLU. The graph represents the mean RLU ± SD of n=3 replicates from representative of two independent experiments and statistics in comparison with PBS control group determined by using one-way ANOVA with P values noted in the figure.