Fig. 2. SSR3 mRNA levels correlate with susceptibility to taxanes in breast cancer patients.
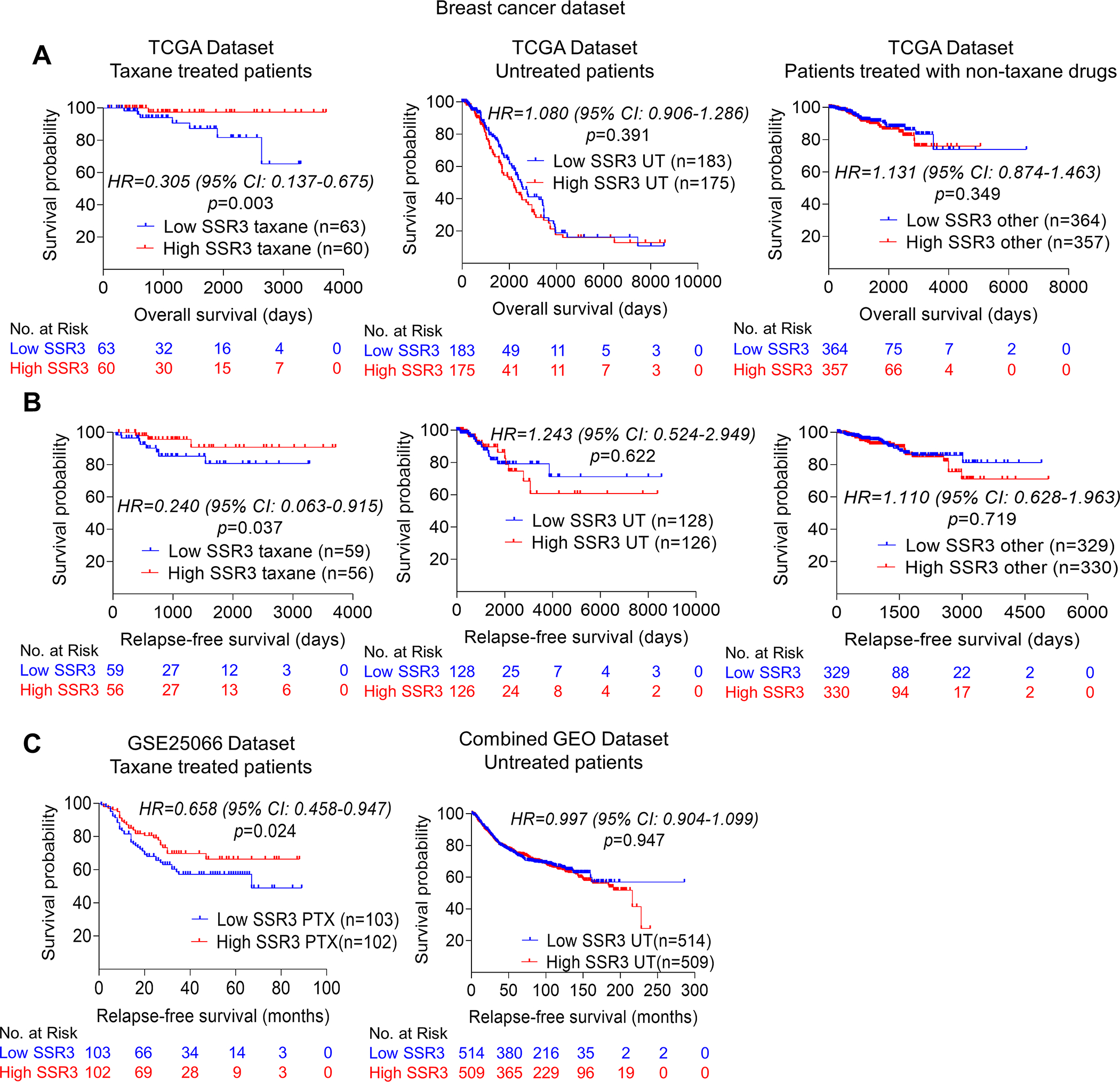
A, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showing the association of high SSR3 mRNA levels with favorable overall survival in TCGA taxane treated breast cancer patients (n=123) and not in patients who did not receive any chemotherapy (n=358) or who received non-taxane chemotherapies (n=722) (https://xena.ucsc.edu/) (23). B, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showing the association of high SSR3 mRNA levels with relapse-free survival in TCGA taxane treated breast cancer patients (n=115) and not in patients who did not receive any chemotherapy (n=254) or who received non-taxane chemotherapies (n=659) (https://xena.ucsc.edu/) (23). Taxane treated patients included patients who have received taxol, paclitaxel, docetaxel, ABX and taxotere as indicated in TCGA breast cancer dataset. C, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showing the association of high SSR3 expression with relapse-free survival in the GSE25066 dataset which includes only taxane-treated patients who have not received hormonal therapy (n=205) (24,25). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showing no such association in combined GEO datasets (GSE16716, GSE19615, GSE31519, GSE37946, GSE45255 and GSE65194) which includes patients who have not received hormonal therapy or chemotherapy (n=1023) (26–28). For A, B and C median was used as a cutoff to separate high and low SSR3 expression. p value, Hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were computed using Cox proportional hazards analysis.
