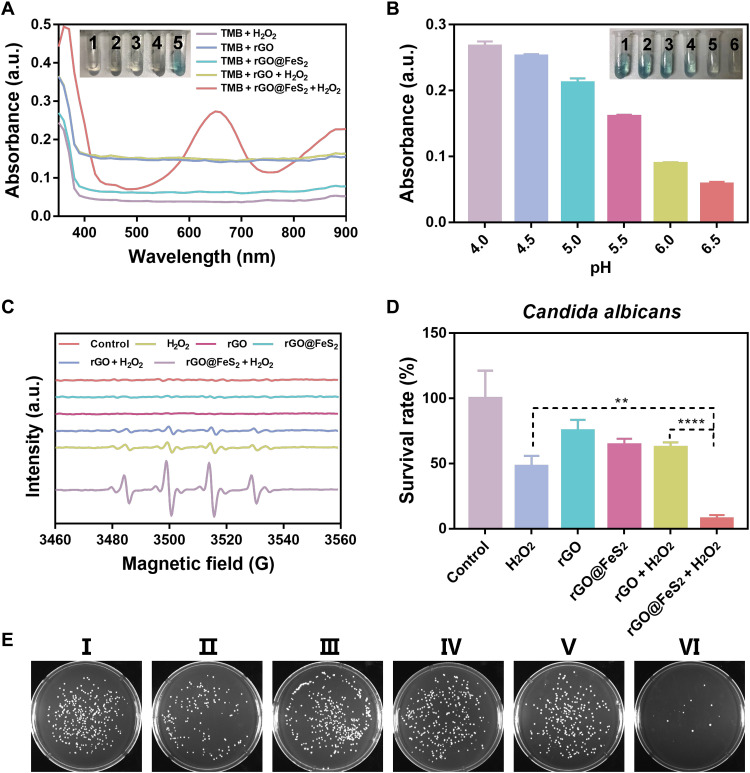
Fig. 3. POD-like and anti–C. albicans activities of rGO@FeS2 nanozymes.
(A) Ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra and corresponding color changes of TMB in different reaction systems: 1, TMB + H2O2; 2, TMB + rGO; 3, TMB + rGO@FeS2; 4, TMB + rGO + H2O2; 5, TMB + rGO@FeS2 + H2O2 in a pH 4.5 HAc-NaAc buffer after 15 min of incubation. (B) pH-dependent POD-like activities of rGO@FeS2. The pH values of insets 1 to 6 are 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, and 6.5. (C) EPR monitoring the generation of •OH by rGO@FeS2 in the presence of H2O2 in a pH 4.5 HAc-NaAc buffer after 5 min of incubation. (D) Antifungal effects of rGO@FeS2 and H2O2 on C. albicans. (E) Digital images of C. albicans colonies after different treatments. I to VI correspond to the x coordinate of (D), respectively. An 80 μM amount of H2O2, rGO, and rGO@FeS2 at 25 μg/ml was used for anti–C. albicans at 37°C for 120 min. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 3). **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001.