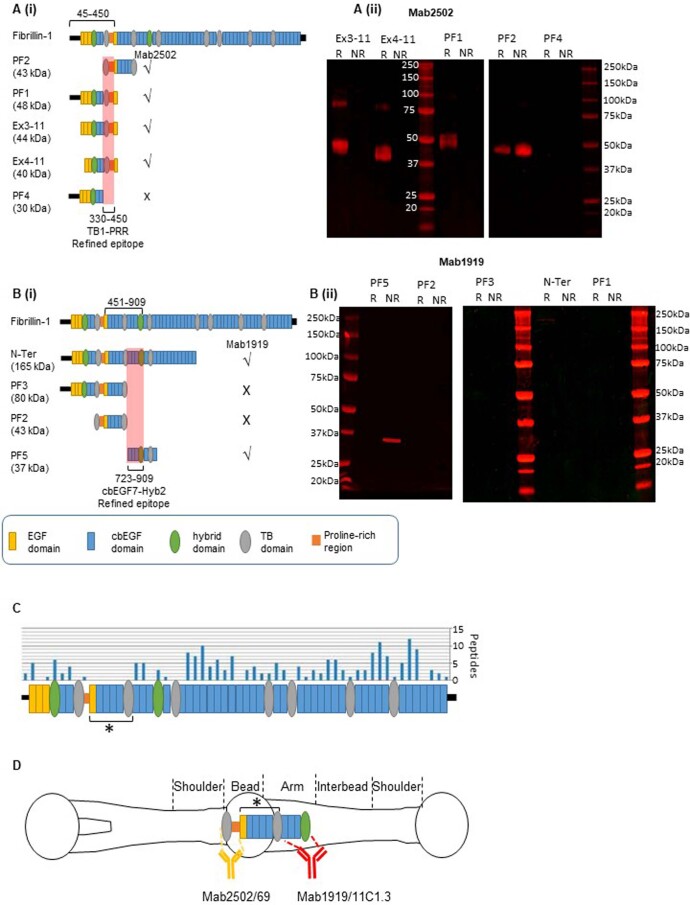
Extended Data Fig. 2. Refining epitope labelling of fibrillin recombinant fragment.
Mab2502 (clone 26 (epitope within residues 45–450 from epitope mapping13)) and Mab1919 (clone 11C1.3 (epitope within residues 451–909 as defined by manufacturer)) were used to probe overlapping recombinant fibrillin fragments to more accurately define their epitopes in fibrillin-1. (Ai and Bi) schematic diagrams of recombinant fragments N-Ter, PF1, PF2, PF3, PF4, PF5, Ex3-11 and Ex4-11. Recombinant fibrillin-1 fragments after separation by SDS-PAGE in the presence (R) or absence (NR) of a reducing agent followed by western blotting with either (Aii) Mab2502 or (Bii) Mab1919. These blots were repeated at least 3 times. The antibody epitopes for mab2502 (45–45013) and mab1919 (451–909) are narrowed down to TB1-PRR (residues 330–450) and cbEGF7-Hyb2 (residues 723-909) respectively, highlighted in red. (C) Number of peptides identified by LC-MS/MS from each domain of fibrillin, where a protease resistant region is located between TB1 to TB2 (TB domains are numbered) and indicated by an asterisk (redrawn from41). (D) Diagram of the fibrillin microfibril repeating unit with the binding sites of Mab2502 and Mab1919 in adult human ciliary zonule microfibrils (as determined in38) and putative location of the protease resistant region identified in41. Panel c adapted from ref. 41 under a Creative Commons licence CC BY 4.0.