Figure 2.
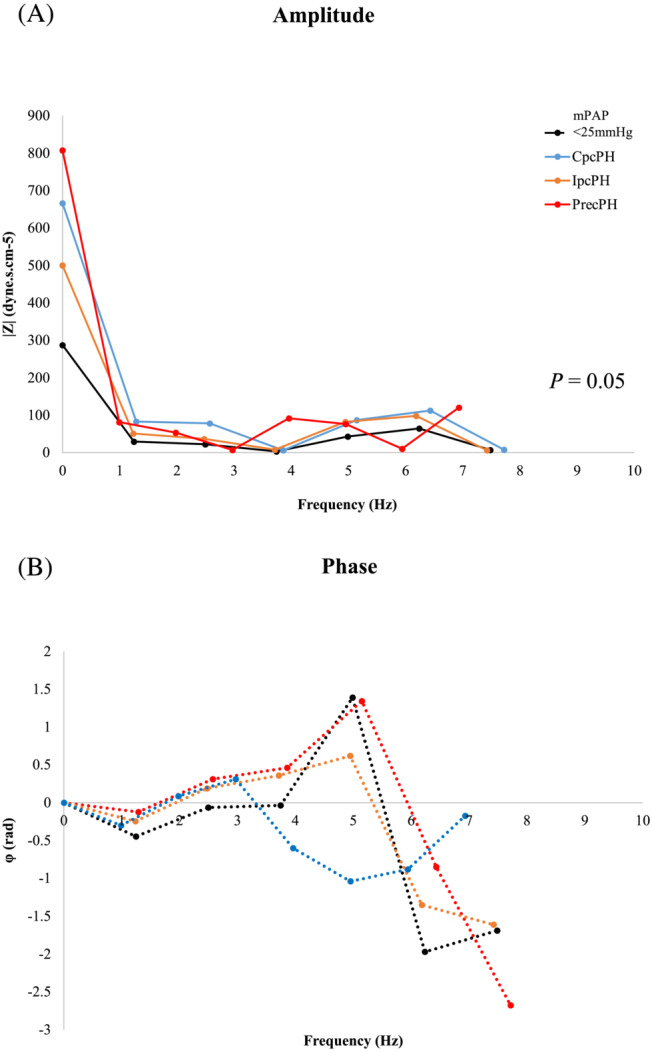
Ensemble average pulmonary Zc spectra graphed as its (A) amplitude and (B) phase in different PH study populations (mPAP <25 mmHg patients are represented in black). Pulmonary Zc is a frequency (Hz)‐dependent function encompassing information about resistive, capacitive, and inertial components of vascular hydraulic load as well as the extent of pulse wave reflection. Results are reported as spectra of amplitude and phase vs. frequency (Hz). Pulmonary Zc spectra in all patients with PH demonstrate increases of both the steady component (increased resistance) and oscillatory component (elevated pulmonary Zc as well as increased pulse wave reflection) of hydraulic load. In mPAP <25 mmHg patients (black), the first minimum occurred around 1 Hz, with little variability in the spectra, including the zero‐frequency term (i.e. PVR) and pulmonary Zc. The phase remained close to zero until 2 Hz, after which it was more positive. The average pulmonary Zc was approximately 37% of the PVR. In IpcPH patients (orange), the impedance spectra resembled that of mPAP <25 mmHg patients with the first minimum occurring around 1 Hz. IpcPH patients, however, had slightly higher amplitudes of pressure for each harmonic, with the phase progressively positive after 2 Hz. The average pulmonary Zc was approximately 42% of the PVR. In PrecPH patients (red), the pulmonary Zc spectra appeared qualitatively similar to that of the systemic circulation. Amplitudes of harmonics of pressure and flow were higher, with more variability, less rounded waveforms, and steeper phase angles. The first minimum occurred around 1 Hz, and the second minimum at 5 Hz. The average pulmonary Zc was approximately 17% of the PVR. The phase remained close to zero until 2 Hz, after which it became positive. In CpcPH patients (blue), amplitudes of harmonics of pressure and flow were also higher than control and IpcPH cohorts, albeit with less variability and a pulmonary Zc to PVR ratio of 23%. CpcPH, combined pre‐capillary and post‐capillary PH; IpcPH, isolated post‐capillary PH; PH, pulmonary hypertension; PrecPH, pre‐capillary PH; PVR, pulmonary vascular resistance; Zc, characteristic impedance.
