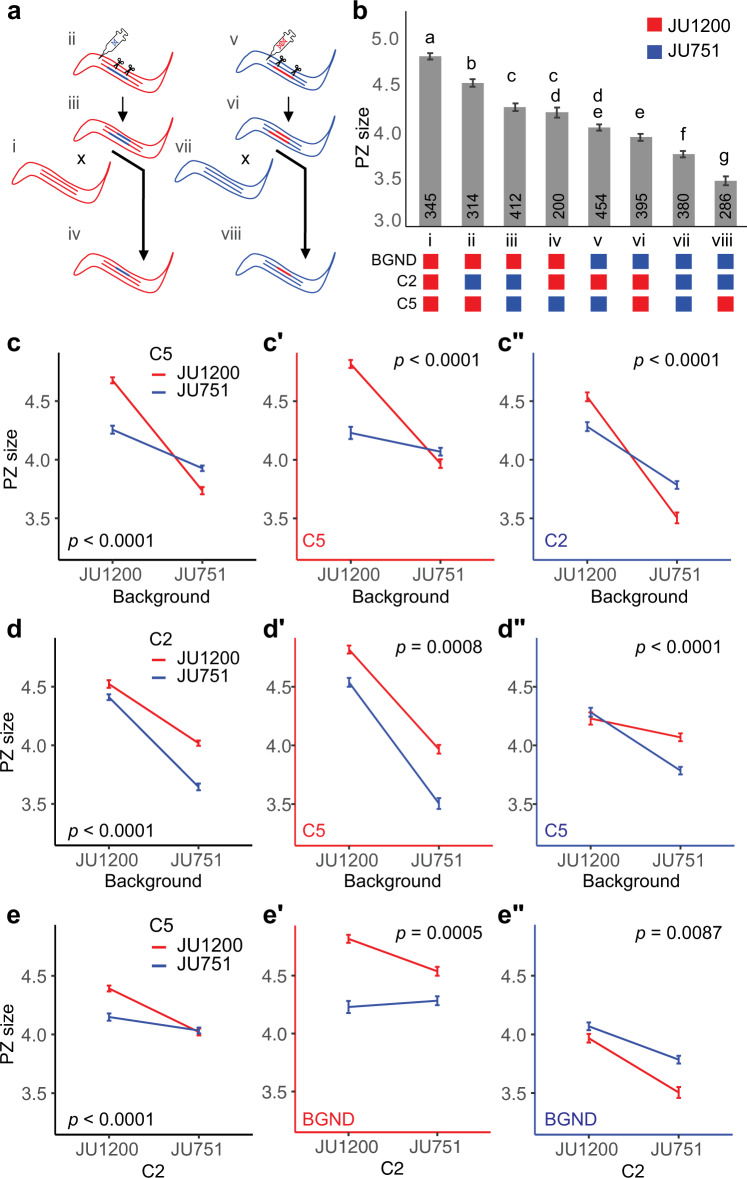
Fig. 6. Higher-order epistatic interactions shape natural variation in PZ size.
a Scheme depicting the generation of the eight genotypes used in the interactions analysis. The different genotypes were derived by made either creating or replacing the lag-2(cgb1007) deletion in JU1200 and JU751 background NILs. The successfully modified lines were then backcrossed to the parental lines to isolate the CRISPR modifications in the parental backgrounds. Genotypes are labelled i-viii for clarity. b Estimated marginal means ± standard errors of PZ size from a generalized linear model describing a data set containing all eight genotypes. JU1200 and JU751 genotypes are indicated by red and blue, respectively, and are indicated for each of the loci and background below the chart. Crossbars and error bars represent estimated marginal means ± standard errors from a generalized linear model (two-sided). Lowercase letters indicate significant (p < 0.05) Tukey-adjusted pairwise contrasts such that groups that share a letter are not significantly different. n-values across six blocks for each genotype are indicated in the bars. c–e The same model-derived means ± standard errors as in panel b presented to show interactions among the loci and background. Graphs with black axes show only two-way interactions. The third dimension is represented as a split into two graphs with red and blue axes indicating the genotypes for the locus given in the bottom left. Two-way interaction p-values are given in the graphs. Analyses were carried out on raw data (PZ area in pixels), but the y-axes were scaled to μm2 for presentation (0.0504 μm2/pixel) (see Supplementary Note 11 for model details). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.