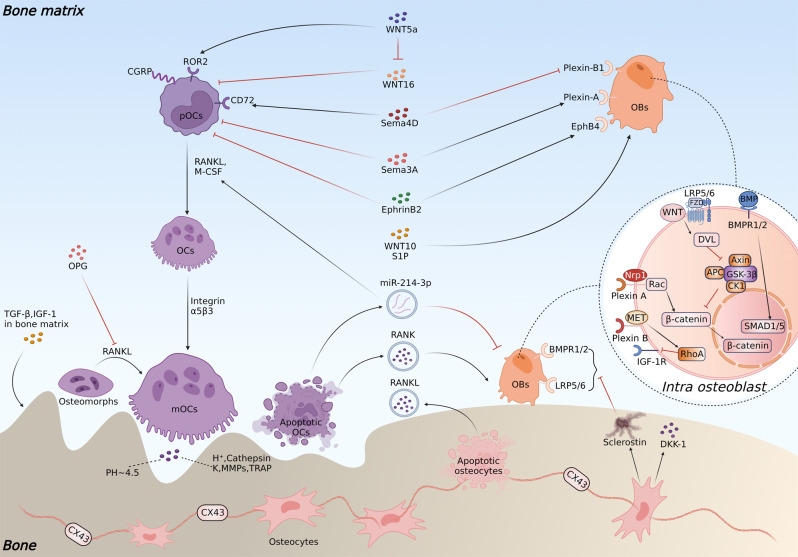
Fig. 5.
Cellular crosstalk among osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes during the remodeling process. Osteoblast- and osteocyte-derived OPG can suppress the fusion of osteomorphs into osteoclasts. Sema4D promotes osteoclastic resorption by binding CD72 on pOCs, while Sema3A, produced by osteocytes and osteoblasts, inhibits osteoclastogenesis. WNT5a expressed by osteoblasts can stimulate the differentiation of pOCs in the noncanonical pathway by binding to ROR2 and reversing the inhibitory effects of WNT16 on RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. EphrinB2 secreted by osteoclasts can bind to EphB4 on osteoblasts and promote osteogenic differentiation by inhibiting the small GTPase RhoA, whereas reverse Eph signaling on pOCs can inhibit osteoclastogenesis by downregulating c-FOS and NFATc1 expression. Apoptotic osteoclasts secrete miR-214-3p, which suppresses osteoblast-specific transcription factors such as Osterix and ATF4 and promotes osteoclastogenesis by decreasing PTEN through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Conversely, RANK secreted by apoptotic osteoclasts can activate Runt-related transcription factor 2 and the intracellular PI3K-Akt-mTORC1 pathway. Sclerostin secreted by osteocytes can inhibit osteogenesis by binding to the LRP5/6 coreceptor to promote GSK3β complex-mediated inhibition of anabolic β-catenin signaling and inhibiting BMP-2/SMAD1/5-induced osteogenesis. Osteocyte apoptosis is accompanied by the secretion of RANKL, which promotes the resorption process. Sema4D inhibits IGF-1-mediated osteoblastic formation by binding the Plexin-B1 receptor expressed on osteoblasts. Sema3A acts on Plexin-A and neuropilin 1 (Nrp1) on pOBs to promote osteogenesis through the Rac signaling pathway