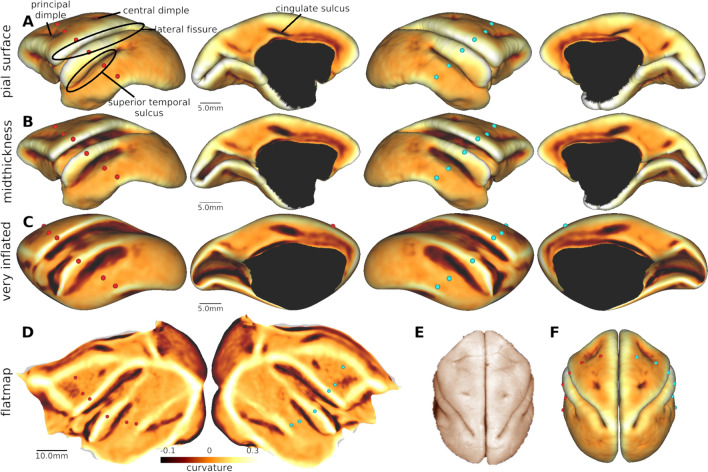
Fig. 1.
Surface models of night monkey cerebral cortex. Cortical curvature displayed on A pial, B mid-thickness and C very inflated surfaces, and D a flatmap. Three sulci (lateral fissure, superior temporal, and cingulate sulcus) and three dimples (principal, arcuate, and central dimple) were consistently identified in all of the animals (N = 9). Dorsal views of (E) postmortem brain (modified image from http://brainmuseum.org/) and (F) reconstructed pial surface. Red dots are placed at regular intervals on the ‘anatomical coordinates’ of the mid-thickness surface. Note that the corresponding red dots are located in a distorted manner in the very-inflated and flat surfaces. The cyan dots in the right hemisphere are vertices with the same ID contralateral to the red dots in the left hemisphere demonstrate symmetrical reconstruction of the cortical surfaces. Dataset is available at https://balsa.wustl.edu/3k7zv