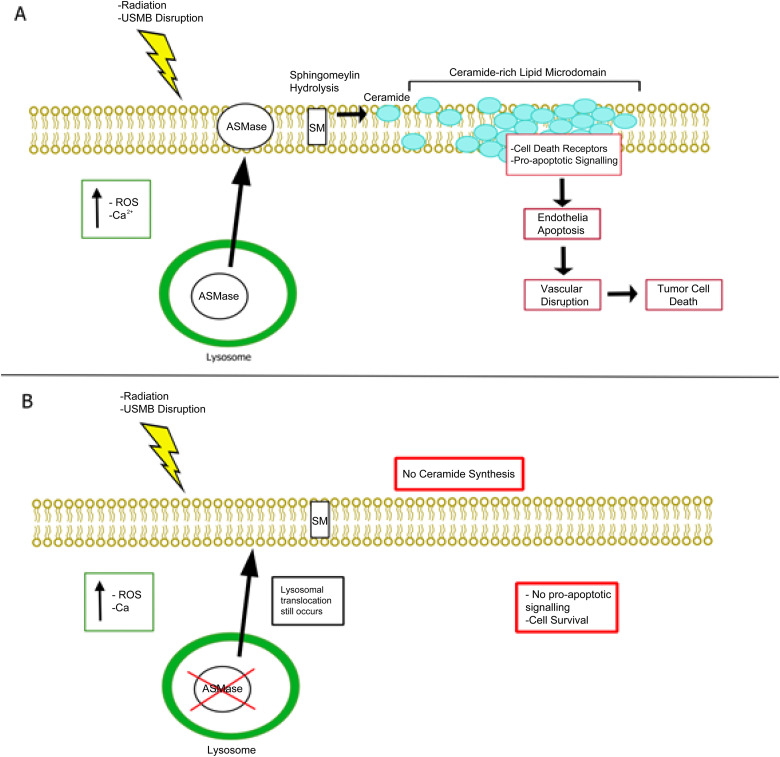
Figure 2.
Mechanism of USMB + RT action. (A) Radiation or plasma membrane disruption induces an increase in oxidative stress and calcium influx resulting in lysosomal translocation and fusion to the plasma membrane. ASMase release into the plasma membrane initiates sphingomyelin hydrolyzation to generate ceramide, resulting in the localization of ceramide-rich lipid microdomains. Plasma membrane alteration in these microdomains result in the localization of cell death receptors and factors resulting in pro-apoptotic signaling, leading to endothelial cell apoptosis, vascular disruption, and eventually tumor cell death. (B) ASMase −/− can resist radiation and USMB leading to vascular preservation and tumor cell survival. When ASMase is knocked out, ceramide is not synthesized, thus no pro-apoptotic signaling occurs in endothelial cells.
Abbreviations: ASMase, acid sphingomyelinase; ASMase −/−, acid sphingomyelinase knockout mice; USMB, ultrasound stimulated microbubble; RT, radiation therapy; Ca2 + , calcium ion; SM, Sphingomyelin.