Figure 2. Tm1 selector Drgx is regulated by Klumpfuss.
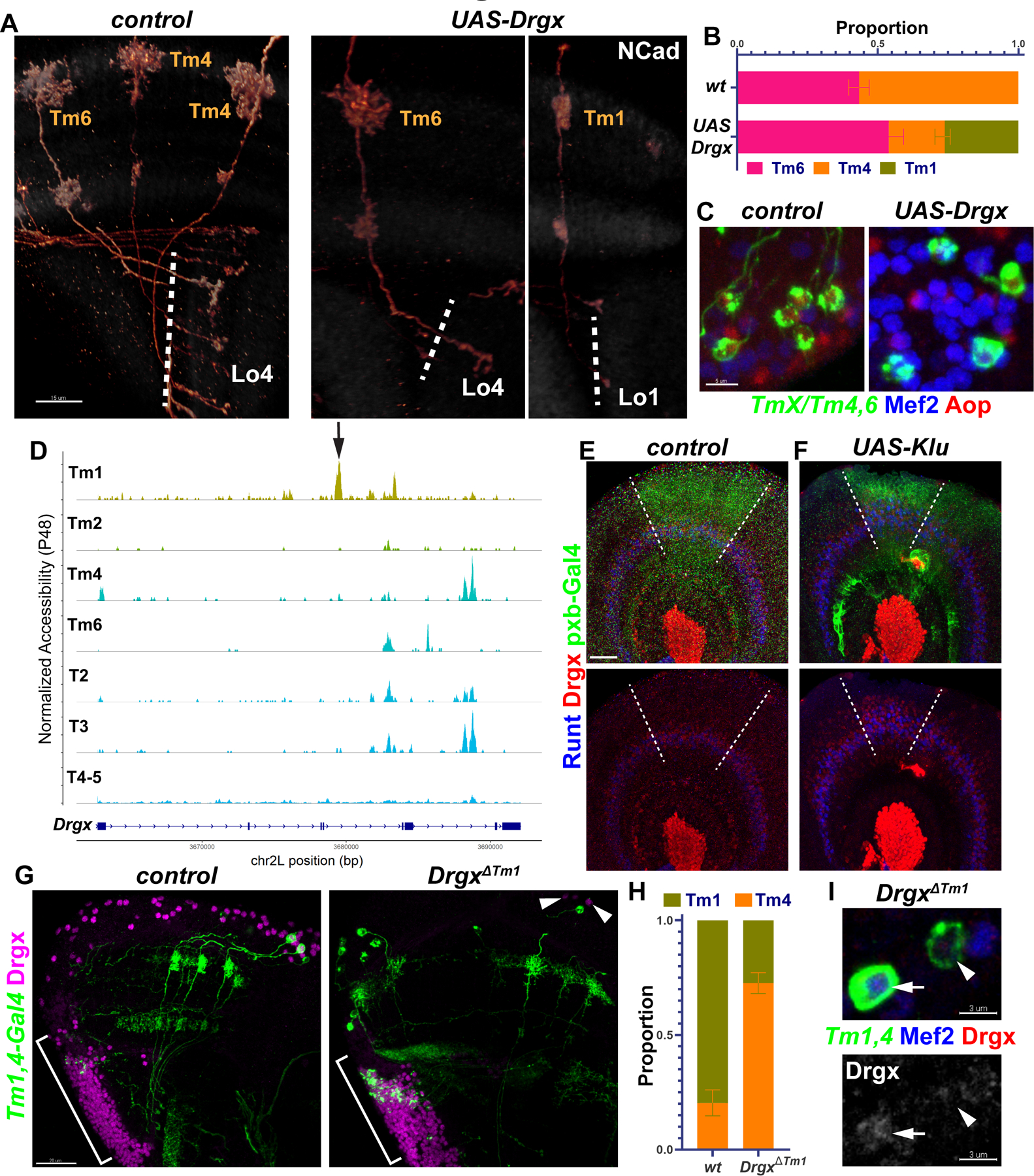
A-C, TmX/Tm4,6-Gal4 driving UAS-Drgx and CD4-tdGFP (flip-out). A, 3D reconstructions of GFP for representative adult neurons, with anti-NCad (white). Dashed lines mark the border of lobula neuropil. B, Quantification of A. n= 92/4 (control), 45/6 (Drgx) neurons/brain, p=0.0003. C, Same as (A) with max. projections of somas with anti-Mef2 (blue) and anti-Aop (red). D, Aggregated accessibility tracks of Drgx locus from the TF-IDF normalized snATAC-seq data at P48 (28). Arrow: Tm1-specific enhancer deleted in (G-I). E-F, pxb-Gal4 driving CD8-GFP and UAS-Klu (F, n=5 brains) in L3 optic lobes, with anti-Runt (blue) and anti-Drgx (red). Dashed lines mark the borders of driver expression. G-I, Tm1,4-Gal4 driving CD4-tdGFP (flip-out) in heterozygous (control) or homozygous DrgxΔTm1 mutants. G, Max projections of adult optic lobes with anti-Drgx (magenta). Brackets mark the location of the lobula plate cortex (T2–5 neurons). Arrowheads: glia (see Fig. S5E) that maintain Drgx expression in the mutants. H, Quantification of G (see also Fig. S5D). Tm1 were normally observed more frequently than Tm4 as the driver expression is much lower in Tm4. n = 57/6 (control) and 181/10 (DrgxΔTm1) neurons/brains, p<0.0001. I, Same as (G), displaying instead somas with anti-Mef2 (blue) and anti-Drgx (red), or only anti-Drgx (bottom). Arrow: Tm1, Arrowhead: Tm4. Scale bars: 15 μm (A,E,F), 5 μm (C), 20 μm (G), 3 μm (I). Error bars denote SEM.
