Fig. 4: TOGA accurately joins genes split in fragmented genome assemblies.
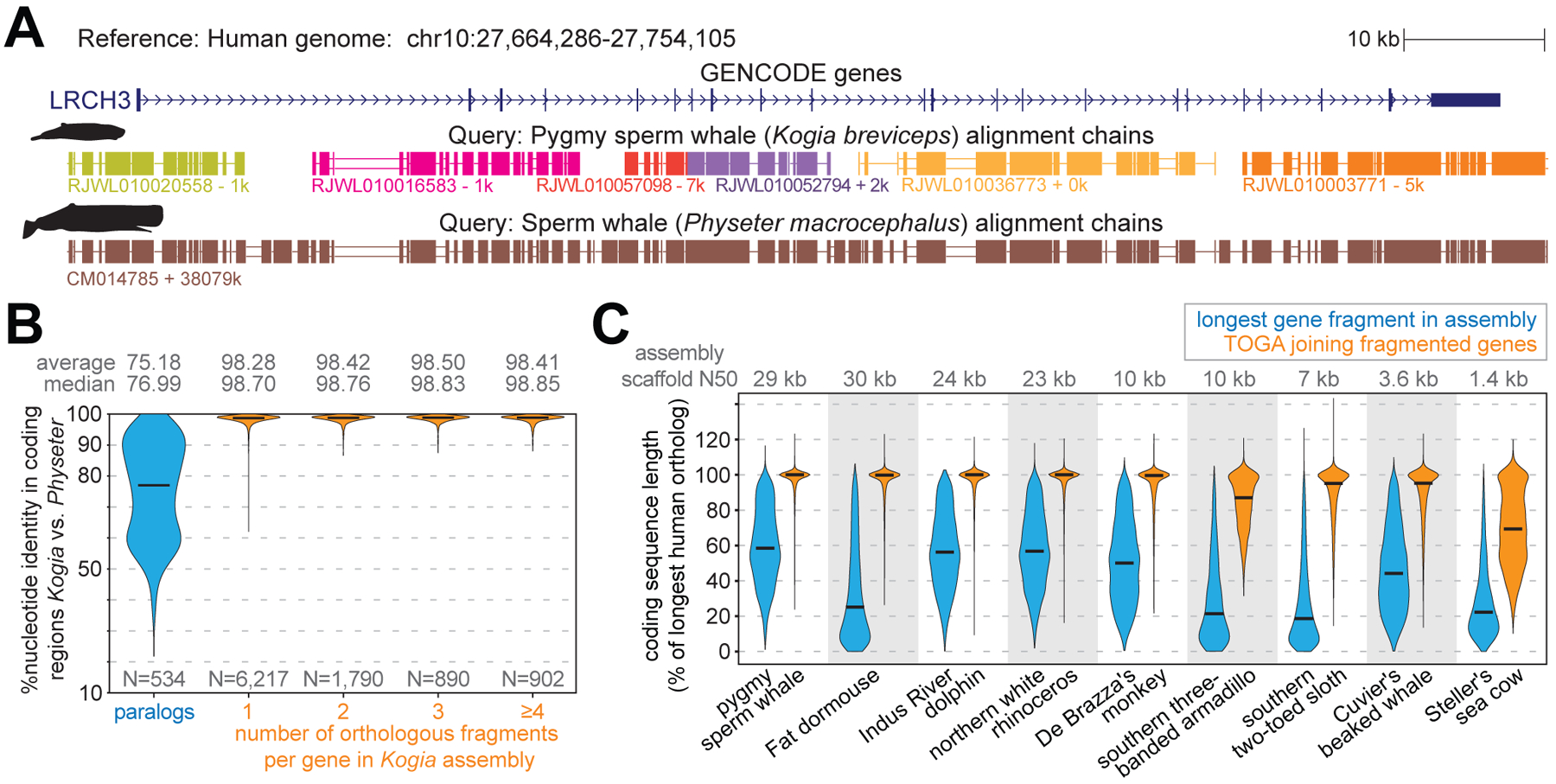
(A) The ortholog of human LRCH3 is split into six fragments (evident by six chains) in the highly-fragmented pygmy sperm whale (Kogia breviceps) assembly (27). Different chain colors represent different scaffolds. TOGA correctly detects and joins all six orthologous gene fragments. The highly-contiguous assembly of the closely related sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus) (29), where LRCH3 is located on a single scaffold, shows a highly-similar alignment block structure.
(B) Violin plots show the coding exon identity between Kogia breviceps and Physeter macrocephalus. Horizontal black lines represent the median. Fragmented orthologs joined by TOGA have an identity distribution highly-similar to orthologs already present on a single scaffold.
(C) Violin plots compare the coding sequence length before (blue) and after joining split genes (orange). Length is relative to the longest transcript of the human ortholog. Codon insertions can increase the relative length to >100%.
