Figure 1.
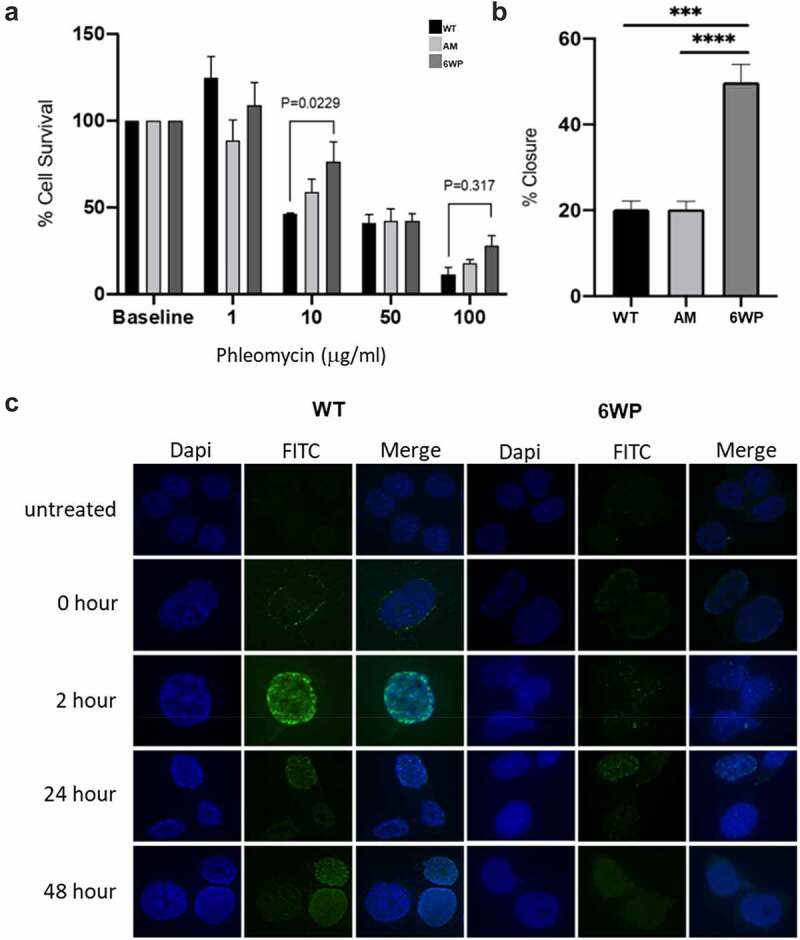
Repeated DNA damage increases cell survival and invasive potential. A) 22Rv1 cells were treated daily with 1 μg/ml of phleomycin for 6 weeks (6WP) or left untreated (WT, AM). A total of 1000 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of phleomycin for 1 hour. Colonies were stained following 12 d of growth and percentage survival was calculated. The mean and SEM of three biological replicates is shown. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA and Sidak’s post-test. *P < 0.05. B) WT, AM and 6WP cells were grown on chamber slides, scratched, and imaged at 0 and 48 hours. Results represent the percentage of the scratch width covered by migration at 48 hours relative to 0 hours. The mean and SEM of 3 biological and 3 technical replicates are shown. Significance was determined using a Student’s one-tailed t-test. *** P < 0.0001. C) Immunofluorescence staining for γH2A.X foci (FITC) in WT and 6WP cells following recovery from phleomycin-induced DNA damage at the indicated time points.
