Fig. 3.
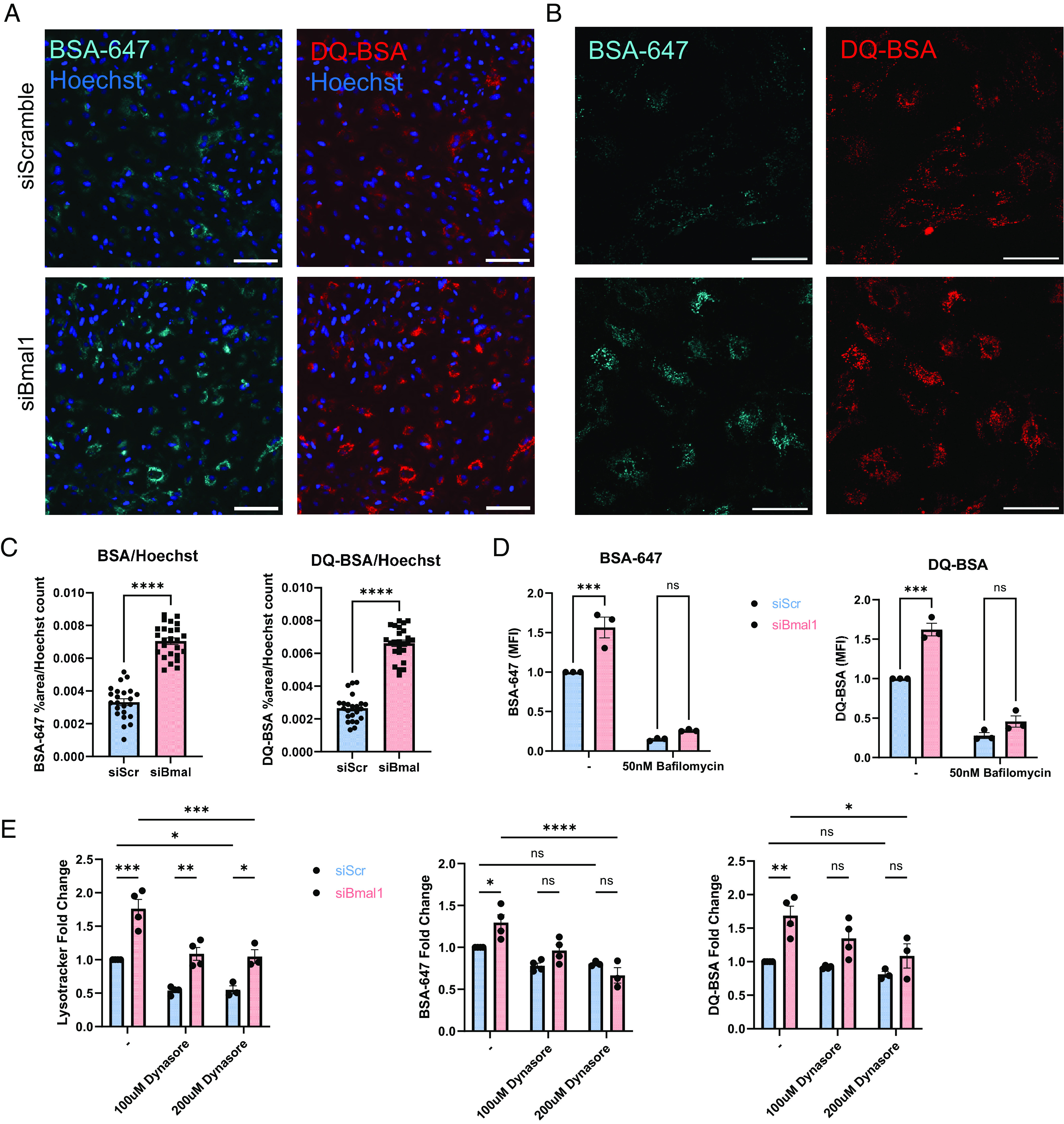
Bmal1 deletion in astrocytes boosts extracellular protein uptake and degradation. (A) 10X epifluorescence live cell imaging of siScramble and siBmal1 astrocytes treated with 1 µg/mL BSA-647 and DQ-BSA for 3 h. (Scale bars, 100 µm.) (B) Example 40X confocal live cell imaging of siScramble and siBmal1 astrocytes treated with 1 µg/mL BSA-647 and DQ-BSA for 3 h. (Scale bars, 50 µm.) (C) Quantification from epifluorescence imaging of BSA-647 and DQ-BSA uptake in live siScramble and siBmal1 astrocytes, %area above threshold normalized to Hoechst cell count per field of view. N = 23 to 25 wells per condition, representative of two independent experiments. (D) Flow cytometry quantification of BSA-647 and DQ-BSA uptake in live siScramble and siBmal1 astrocytes treated with serum-free medium or 50nM Bafilomycin for 3 h. N = 3 independent experiments, MFI normalized per experiment to serum-free media-treated siScramble controls. (E) Flow cytometry quantification of Lysotracker, BSA-647, and DQ-BSA in siScramble and siBmal1 astrocytes treated with either serum-free medium, 100 µM Dynasore, or 200 µM Dynasore for 3 h during BSA incubation. N = 3 to 4 independent experiments, MFI normalized per experiment to serum-free media-treated siScramble controls. (D and E) * =P < 0.05, ** =P < 0.005, *** =P < 0.0005, **** =P < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA with Sidak multiple comparisons test.
