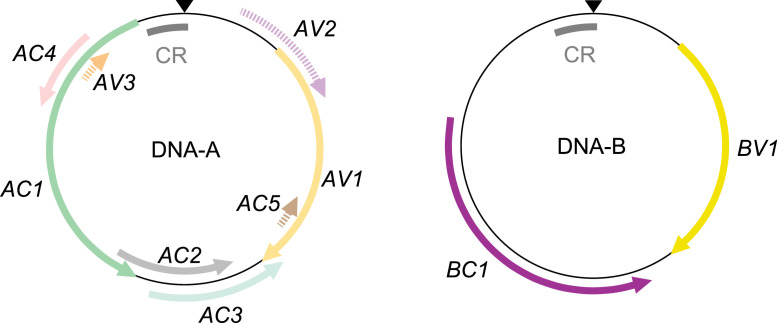
Fig. 1.
Begomovirus DNA-A and DNA-B segments and open reading frames (ORFs). Both genomic segments are ambisense: some genes are encoded on the virus sense strand (V, the strand that is encapsidated), and others are encoded on the opposite complementary sense strand (C). Bipartite begomovirus DNA-As contain at least five functional ORFs. Only one of the required five genes is encoded in the virion sense—AV1 encodes the coat protein. In the complementary sense, AC1 encodes the replication-associated protein, AC2 encodes the transcriptional activator protein, AC3 encodes the replication enhancing protein and AC4 encodes an RNA-silencing suppressor. Some DNA-A molecules have additional ORFs, shown with dashed lines to indicate that they are not always present or functional. The AV2 ORF present in OW begomoviruses encodes a pre-coat protein that functions in movement. AC5 and AV3 are inconsistently annotated ORFs that encode silencing suppressors (Gong et al., 2021). The extent to which AC5 and AV3 function is conserved across the begomovirus phylogeny is unknown (Zhao et al., 2022; Li et al., 2015). DNA-B is also ambisense. BV1, on the virion sense strand, encodes the nuclear shuttle protein NSP and BC1, on the complementary strand, encodes the movement protein MP (Fondong, 2013; Hanley-Bowdoin et al., 2000). An additional BV1-overlapping ORF (BV2), thus far only described in a single species (Chiu et al., 2022) is omitted. The homologous common region containing the origin of replication nick site (black triangle) is denoted CR.