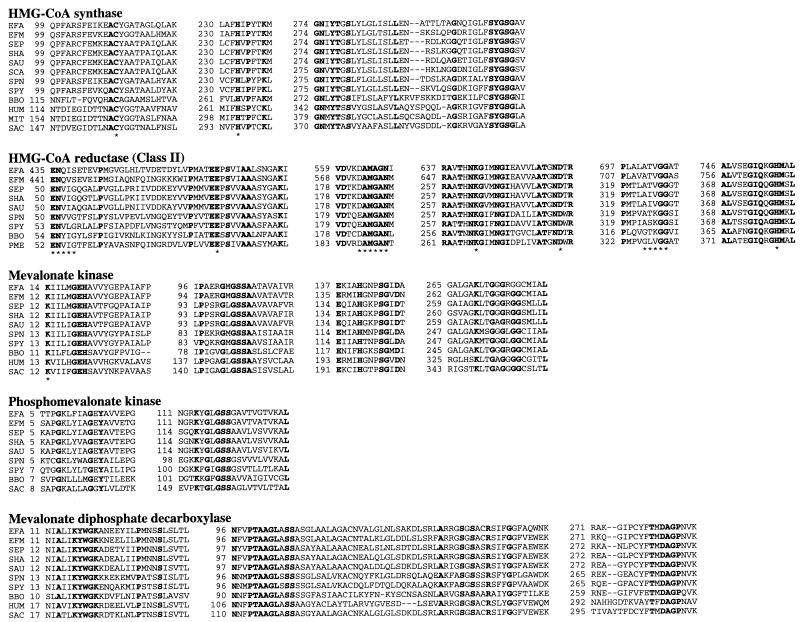
FIG. 2.
Alignment of the conserved regions of the mevalonate pathway enzymes from gram-positive bacteria, B. burgdorferi, P. mevalonii, and eukaryotes. Bold type indicates that amino acids are identical in all proteins. The asterisks indicate amino acids proposed to function in catalysis and substrate binding. Dashes indicate gaps introduced into the sequence to optimize the alignment. Numbers refer to amino acid positions. In all alignments, abbreviations are as follows: EFA, E. faecalis; EFM, E. faecium; SEP, S. epidermidis; SHA, S. haemolyticus; SAU, S. aureus; SPN, S. pneumoniae; SPY, S. pyogenes; BBO, B. burgdorferi (AE001169). In HMG-CoA synthase, abbreviations are as follows: SCA, Staphylococcus carnosus (U450157); HUM, human cytoplasmic enzyme (Q01581); MIT, human mitochondrial enzyme (NP005509); SAC, S. cerevisiae (P54839). In HMG-CoA reductase, abbreviations are as follows: PME, P. mevalonii (P13702). In mevalonate kinase, abbreviations are as follows: HUM, human (NP000422); SAC, S. cerevisiae (NP000422). In phosphomevalonate kinase, abbreviations are as follows: SAC, S. cerevisiae (P24521). In mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase, abbreviations are as follows: HUM, human (AAC50440); SAC, S. cerevisiae (AAC49252).