Figure 2:
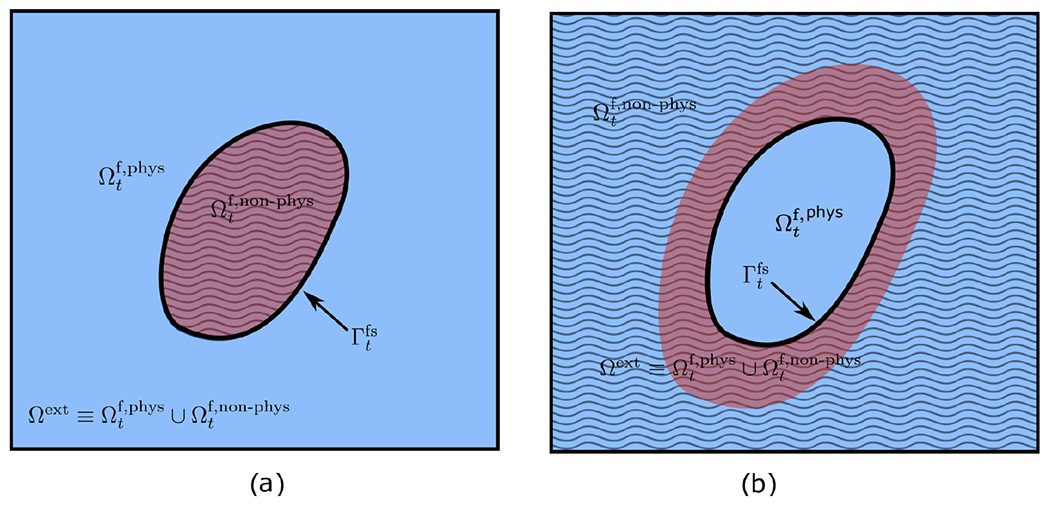
In the immersed Lagrangian-Eulerian method, the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations are solved on an extended computational domain that incorporates both fluid and solid subregions, and is split into a physical and a nonphysical fluid regions. (a) In this configuration a simply connected domain represents the volumetric structure that is immersed in the fluid. The non-physical fluid region in this case is the region occupied by the solid and shown by wavy stripes. (b) In this case, the physical fluid region is enclosed by the thick shell-like structure of the solid. The non-physical domain (shown by wavy stripes) includes the solid domain in addition to an extended region to obtain a fixed Cartesian computational domain.
