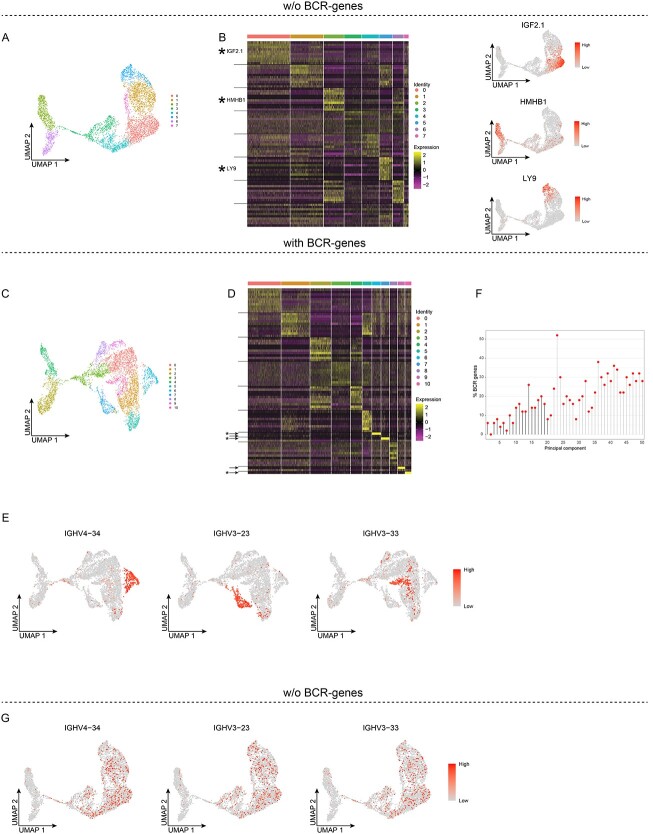
Figure 4.
BCR-genes influence unsupervised clustering of bone marrow early B-lineage cells. A and B, Unsupervised clustering without BCR-genes. A, UMAP projection and unsupervised clustering of BM early B-lineage cells. B, Heat map displaying the scaled relative expression levels of the top-10 significantly up-regulated genes in each cluster (Bonferroni-adjusted P-values <0.05 of the Seurat negative binomial generalized linear model). Gene list in Table S3. The black horizontal lines indicate which DEGs are found in each cluster. C-F, Unsupervised clustering with BCR-genes retained. C, UMAP projection and unsupervised clustering. D, Heat map displaying the scaled relative expression levels of the top-10 significantly up-regulated genes in each cluster (Bonferroni-adjusted P-values <0.05 of the Seurat negative binomial generalized linear model). The asterisks indicate genes plotted in E, the arrows indicate the BCR-genes, and the black horizontal lines indicate which DEGs are found in each cluster. Gene list in Table S3. E, UMAP projection of all the cells, coloured according to scaled gene expression level. F, Lollipop plot displaying the percentages of BCR TCR-genes among the top-50 genes in the first 50 PCs; PCs used for unsupervised clustering are indicated by black stems. G, UMAP projection of BM early B-lineage cells clustered without BCR-genes, whereby the BCR-genes were added back, and their scaled gene expression is shown.