Figure 4.
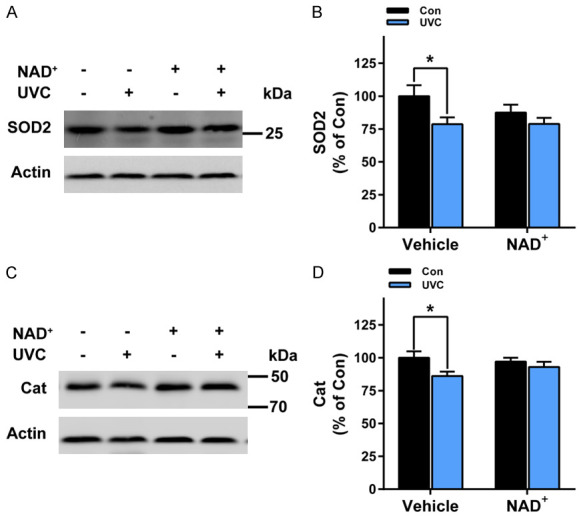
NAD+ administration significantly attenuated UVC-induced decreases in the levels of SOD2 and catalase in the mice’s skin. A, B. UVC induced significant decreases in SOD2 levels in the mice’s skin, which was significantly attenuated by the NAD+ administration. N = 16; *, P < 0.05. C, D. UVC induced significant decreases in catalase levels in the mice’s skin, which was significantly attenuated by the NAD+ administration. After the mice were administered with 1 mg/kg NAD+, the mice were exposed to UVC irradiation at the dosages of 0.6 J/cm2. One hr after the irradiation, the SOD2 levels and the catalase levels of the skin was determined by Western blot assays. N = 6. *, P < 0.05.
