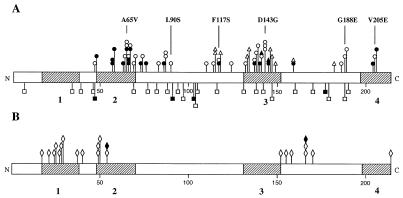
FIG. 1.
cheZ mutations resulting in a nonchemotactic phenotype. The CheZ protein is shown, with locations of amino acid substitutions resulting from mutations indicated. Cross-hatched regions, regions conserved among E. coli, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, P. aeruginosa, and P. putida with the following proposed functions: 1, unknown; 2, unknown; 3, oligomerization (4); 4, CheY binding (3). (A) Loss-of-function mutations, which result in an increase in the CW bias of flagellar rotation. Missense mutations are above the bar; nonsense and frameshift mutations are below. ○, complete loss-of-function missense mutations from this study; ●, partial loss-of-function missense mutations from this study; ▵ and ▴, missense mutations from reference 33 and from references 4 and 40, respectively; □ and ■, nonsense and frameshift mutations from this study and reference 40, respectively. The six mutant proteins chosen for further analysis are indicated. (B) Gain-of-function missense mutations, which result in a decrease in the CW bias of flagellar rotation, from references 33 and 34 (◊) and 17 and 40 (⧫).