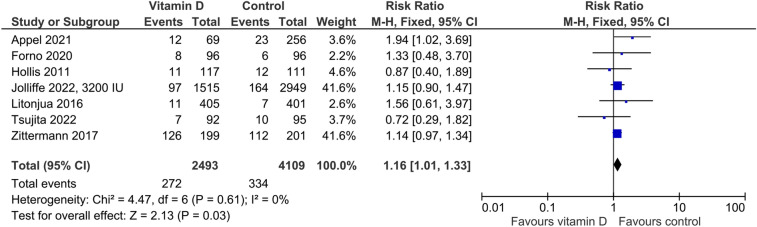
Fig. 6.
Effect of vitamin D on the risk of hospitalization. Data represent the relative risk of hospitalization in vitamin D vs. control with 95% confidence interval of individual studies and total effect. In the figure, the vitamin D dose is given if less than 4000 IU daily or different dosing regimens are used. In all other cases, 4000 IU vitamin D are supplemented. The x-axis indicates the relative risk, ranging from 0.01 to 100. Values < 1 favour vitamin D and values > 1 favour control