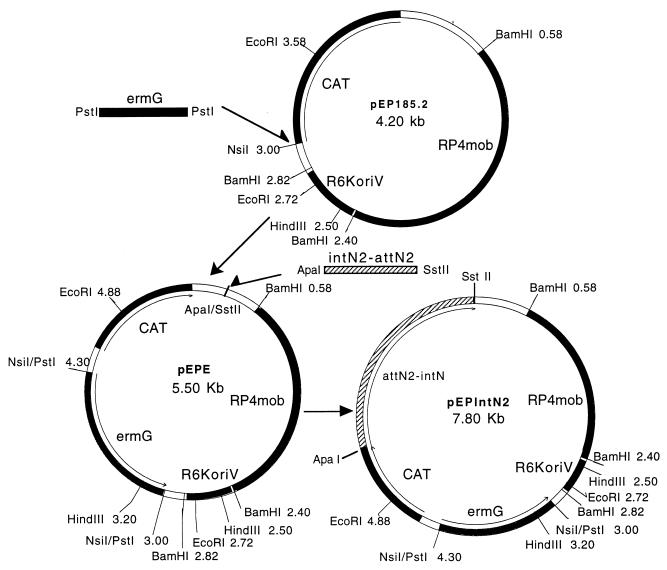
FIG. 1.
Construction of the integration vector, pEPIntN2. An insertional vector that could be used in either Bacteroides or in E. coli was constructed from the pir-dependent mobilizable pEP185.2 (24). The erythromycin-clindamycin resistance gene, ermG, from CTn7853 was PCR amplified with PstI sites encoded in the primers and cloned into the PstI-compatible unique NsiI site on pEP185.2 to form pEPE. pEPE, a Pir-dependent vector, has selectable markers for both E. coli and Bacteroides hosts. The NBU2 integration region, IntN2, consisting of the joined ends, attN2, from the circular form of NBU2 and the adjacent gene, intN2, was PCR amplified from the induced circular form of NBU2. The PCR product was first cloned into pGEM-T (Promega) and sequenced. The 1.8-kbp ApaI-SstII fragment was isolated from pGEM-T and cloned into the ApaI and SstII sites of pEPE to form the NBU2 integration vector, pEPIntN2.