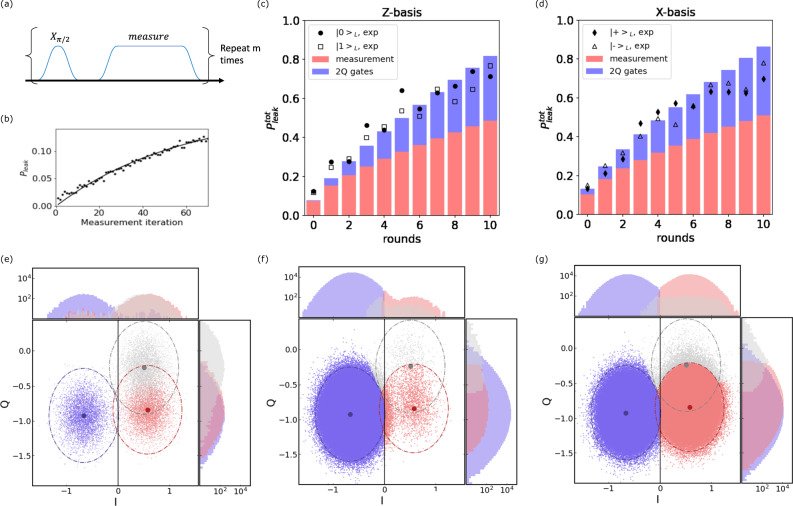
Fig. 5. Leakage analysis.
a Repeated measurement sequence for extracting leakage error during the measurement. The Xπ/2 pulse allows us to randomly sample leakage events from or states. b The leakage probability () to the state measured at QF14. The leakage and seepage rate is obtained by fitting the data with Eq. (15). c, d Qubit leakage in the system as a function of syndrome measurement rounds for Z − and X − basis logical states. Bar plots show the as computed from the gate and measurement leakage rates, obtained from randomized benchmarking (2Q gates) and from the sequence shown in a, respectively. Experimental results, , where paccept is the acceptance probability calculated from the method outlined in Methods “Post-selection method”, are shown as black symbols for comparison. The experimental results plotted here do not include initialization leakage. e Readout calibration data for QF12 (see Fig. 4a). The qubit is prepared in its , , and states and measured. The collected statistics can be seen in as blue (), red (), and grey () where the dot-dashed lines represent 3-σ for each distribution. f 3-state classification results for QF12 after qubit initialization, and g after the first X − syndrome measurement.