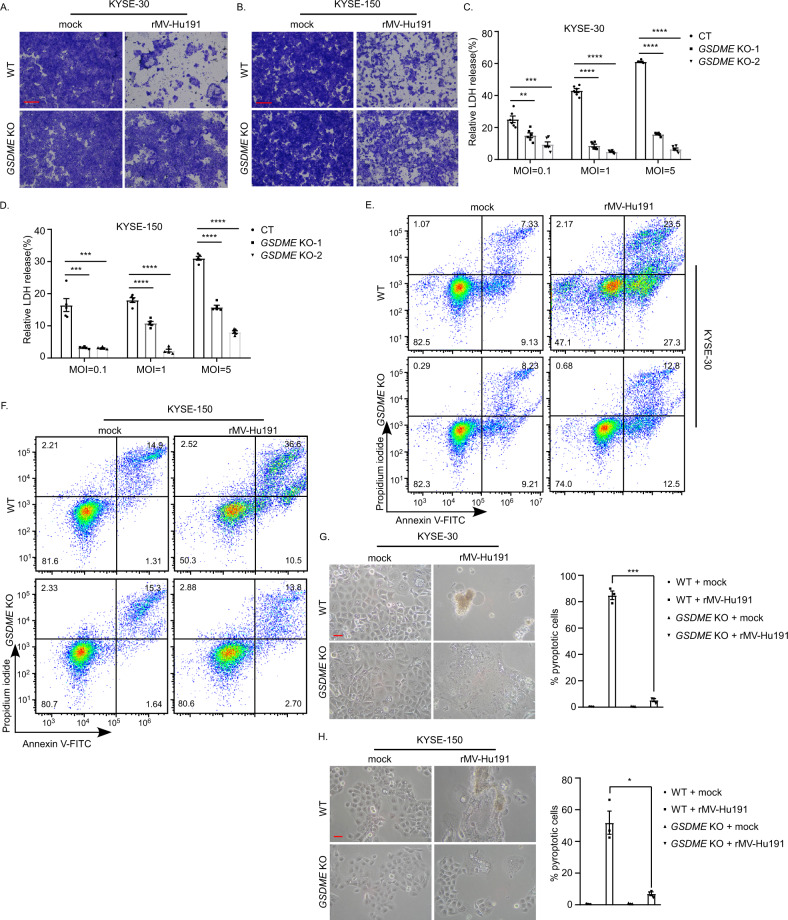
Fig. 3. GSDME mediates rMV-Hu191-induced pyroptosis.
A, B KYSE-30 (A) or KYSE-150 (B) wild-type (WT) and GSDME KO cells were treated with rMV-Hu191 at an MOI of 0.1 for 72 h. Cell-killing efficiency was then determined by crystal staining. The scale bars represent 500 μm. C LDH release in KYSE-30 WT and GSDME KO cells was measured after rMV-Hu191 treatment for 72 h at the indicated doses. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. D LDH release in KYSE-150 WT and GSDME KO cells was measured after rMV-Hu191 treatment for 72 h at the indicated doses. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5). ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. E, F Flow cytometry analysis of Annexin V-FITC/PI-stained KYSE-30 (E) or KYSE-150 (F) WT and GSDME KO cells treated by rMV-Hu191 at an MOI of 0.1 for 48 h. G, H The deficiency of GSDME alleviated the pyroptotic morphology of KYSE-30 (G) and KYSE-150 (H) cells induced by rMV-Hu191. Cells were treated by rMV-Hu191 at an MOI of 0.1 for 72 h. The scale bars represent 50 μm. Pyroptotic cells (cells with large bubbles) were counted from three randomly selected microscopic fields, and the percentage was calculated using the equation pyroptotic cells/total cells × 100%. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test.