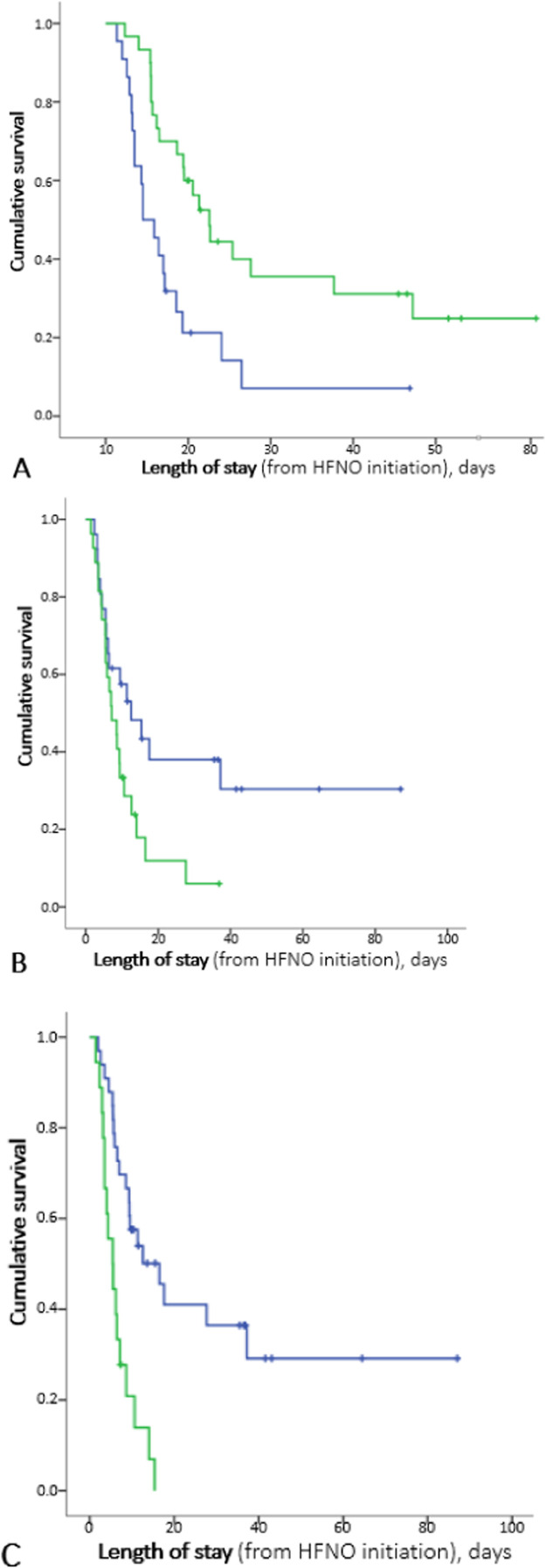
Figure 3.
in-hospital cumulative survival. A: depending on the value of ROX index at D0, compared to threshold (4.88); B: depending on the presence of a CFS score low (2-4) or high (5-7) at admission; C: depending on the presence or absence of signs of respiratory failure before HFNO introduction.
ROX index is calculated by (SpO2/FiO2) / RR (SpO2 is oxygen pulse saturation, FiO2 is fraction of inspired dioxygen, and RR is respiratory rate); HR: hazard ratio; HFNO: high flow nasal oxygen; CFS: clinical frailty scale; clinical signs of respiratory failure include respiratory rate > 30/min, retractions, and abdominal paradoxical breathing pattern.