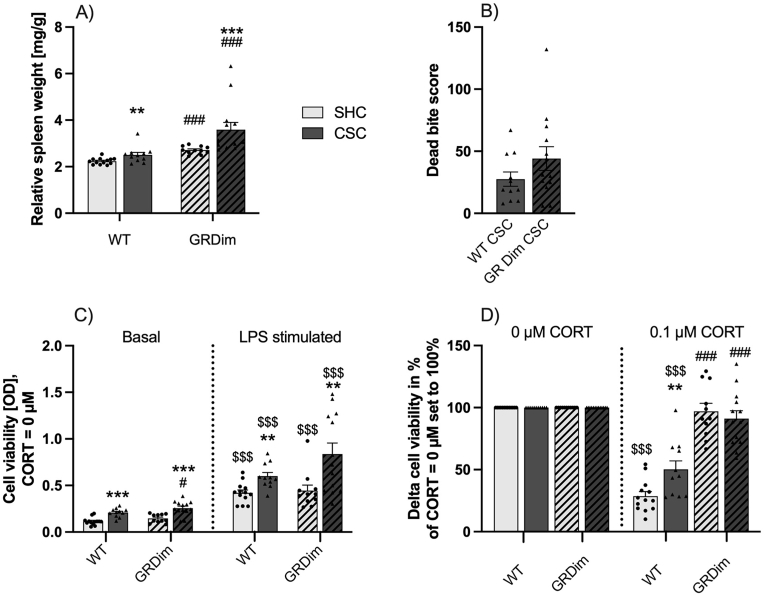
Fig. 5.
Effects on spleen weight and functional splenic in vitro GC sensitivity
When compared to respective single-housed control (SHC; light-grey bars; circles) mice, chronic subordinate colony housing (CSC; dark-grey bars; triangles) increased relative spleen weight (Fig. 5A) in both the wild type (WT; GR+/+; unhatched bars) and GRdim (GRdim/dim; hatched bars) group. Furthermore, relative spleen weight of GRdim SHC and CSC mice was increased compared to respective WT mice. Both, WT and GRdim CSC mice had a bite score above 20 (WT: 27.5; GRdim: 44.2; Fig. 5B). Splenic cell in vitro viability in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS; Fig. 5C) was increased in all groups. Splenocytes from WT and GRdim CSC mice showed a higher basal and LPS-induced cell viability compared to respective SHC mice. Basal cell viability was increased in splenocytes from GRdim vs. WT CSC mice. Delta (LPS - basal) cell viability (0 μM corticosterone (CORT) set to 100%; Fig. 5D) in response to 0.1 μM CORT was reduced in WT SHC and CSC mice when compared to the 0 μM condition. Delta cell viability in response to 0.1 μM CORT was significantly increased in GRdim SHC and CSC vs. respective WT mice, as well as WT CSC vs. SHC mice. Data are presented as bar graphs (mean +SEM) with individual dots. **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 vs. respective SHC. #P ≤ 0.05, ###P ≤ 0.001 vs. respective WT. $$$P ≤ 0.001 vs. respective basal or 0 μM condition.