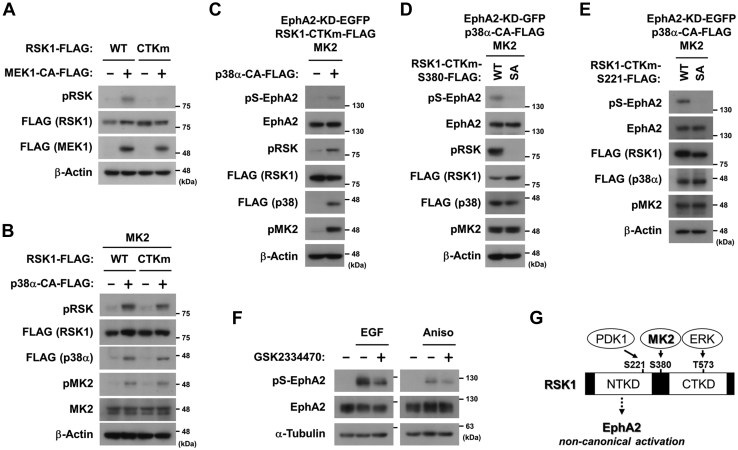
Figure 5.
MK2-induced EphA2 phosphorylation is independent of the CTK activity of RSK.A and B, HEK293 cells were transfected with the expression vectors for FLAG-tagged RSK1 (wild-type (WT) or CTK-dead mutant (CTKm)), FLAG-tagged constitutively activated MEK1 (MEK1-CA-FLAG), MK2, FLAG-tagged constitutively activated p38α (p38α-CA-FLAG), and/or an empty vector. At 24 h post-transfection, whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted with primary antibodies against phospho-RSK at Ser-380 (pRSK), FLAG, pMK2, MK2, and β-Actin. C–E, HEK293 cells were transfected with the expression vectors for EphA2-KD-EGFP, RSK1-CTKm-FLAG (Ser-380 WT, Ala-substitute mutation (SA) or Ser-221 SA), MK2, p38α-CA-FLAG, and/or an empty vector. At 24 h post-transfection, whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted with primary antibodies against pS-EphA2, EphA2, pRSK, FLAG, pMK2, and β-Actin. F, HeLa cells were treated with 10 μM GSK2334470 for 30 min and then stimulated with 10 ng/ml EGF for 10 min or 50 μM anisomycin for 20 min. Whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted with primary antibodies against pS-EphA2, EphA2 and α-Tubulin. G, a schematic diagram of RSK phosphorylation induced by MK2 or ERK. CTK, carboxyl-terminal kinase; EphA2, ephrin type-A receptor 2; MK2, MAPK-activated protein kinase 2; NTK, amino-terminal kinase, RSK, p90 ribosomal S6 kinase.