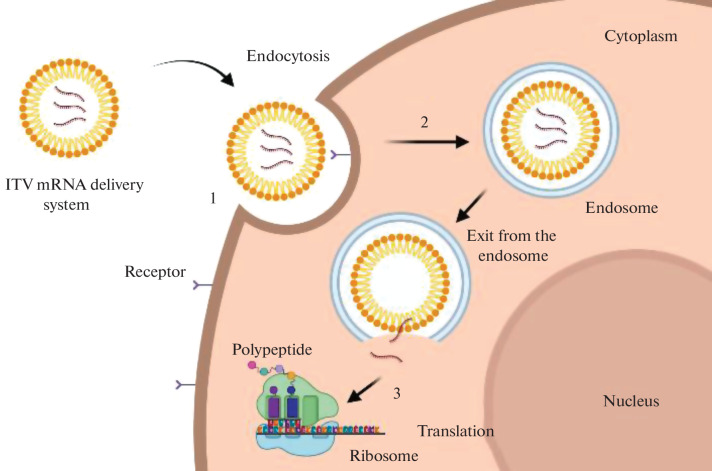
Fig. 10.
Intracellular barriers for in vitro transcribed (IVT) mRNA delivery: (1) interaction between the delivery system and the cell membrane, (2) endocytosis, (3) exit from the endosome and mRNA release to initiate translation. Endocytosis is a mechanism by which extracellular components and fragments of the plasma membrane internalize with the formation of the endocytic vesicle. This process involves vesicles with the internal pH of ~5 known as endosomes which develop from the early endosomes to the late endosomes before fusing with the intracellular organelles called lysosomes. In such a way, particles entering the cell via endocytosis are captured by the endosomes and eventually appear in the lysosomes, where active enzymatic degradation takes place [5, 46].