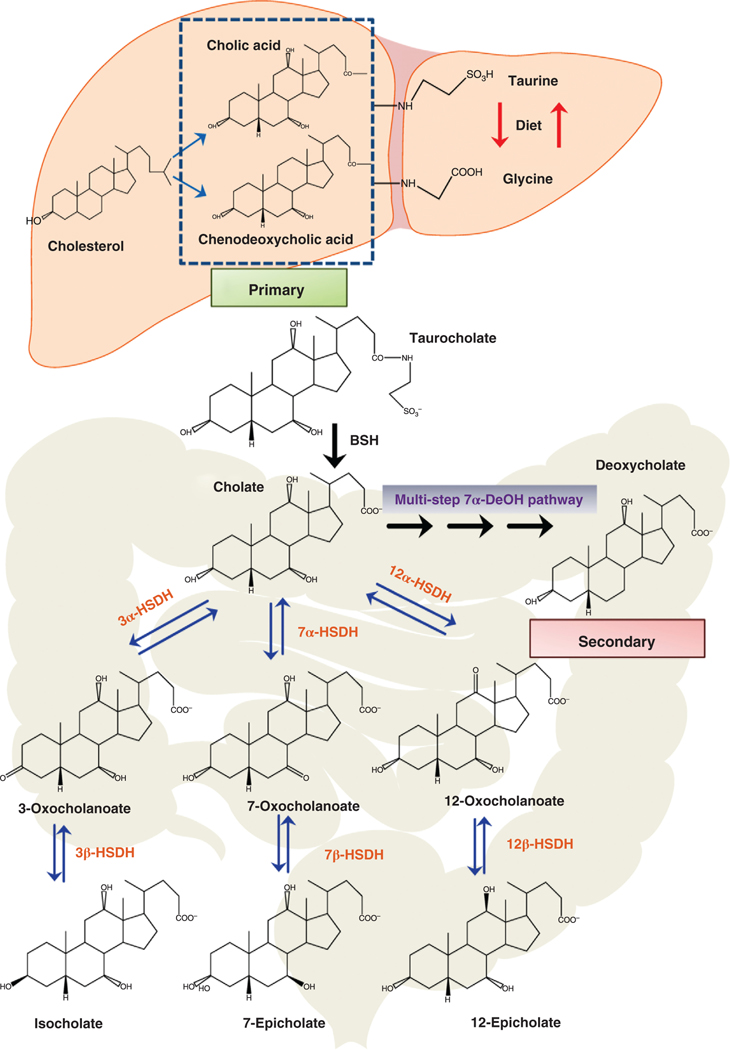
Figure 2. Synthesis of the primary bile acids cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid from cholesterol in liver hepatocytes and metabolism by gut bacteria.
The primary bile acids, cholic acid, and chenodeoxycholic acid are synthesized in the hepatocytes from cholesterol and conjugated with taurine or glycine. Taurocholate is biotransformed by gut bacteria expressing bile salt hydrolases (BSH) to cholic acid and taurine. Gut bacteria can oxidize hydroxyl groups at the 3α, 7α, and 12α position on the steroid ring by 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (3α-HSDH), 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (7α-HSDH), and 12α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (12α-HSDH), respectively. Oxo-bile acids may be further metabolized at the 3β, 7β, or 12β position by 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSDH), 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7β-HSDH) and 12β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (12β-HSDH), respectively, producing iso and epi bile acids. Primary bile acids can be biotransformed to secondary bile acids by removing the 7α-hydroxyl group via a multistep 7α-dehydroxylation (7α-DeOH) biochemical pathway found in some species of the genus Clostridium.