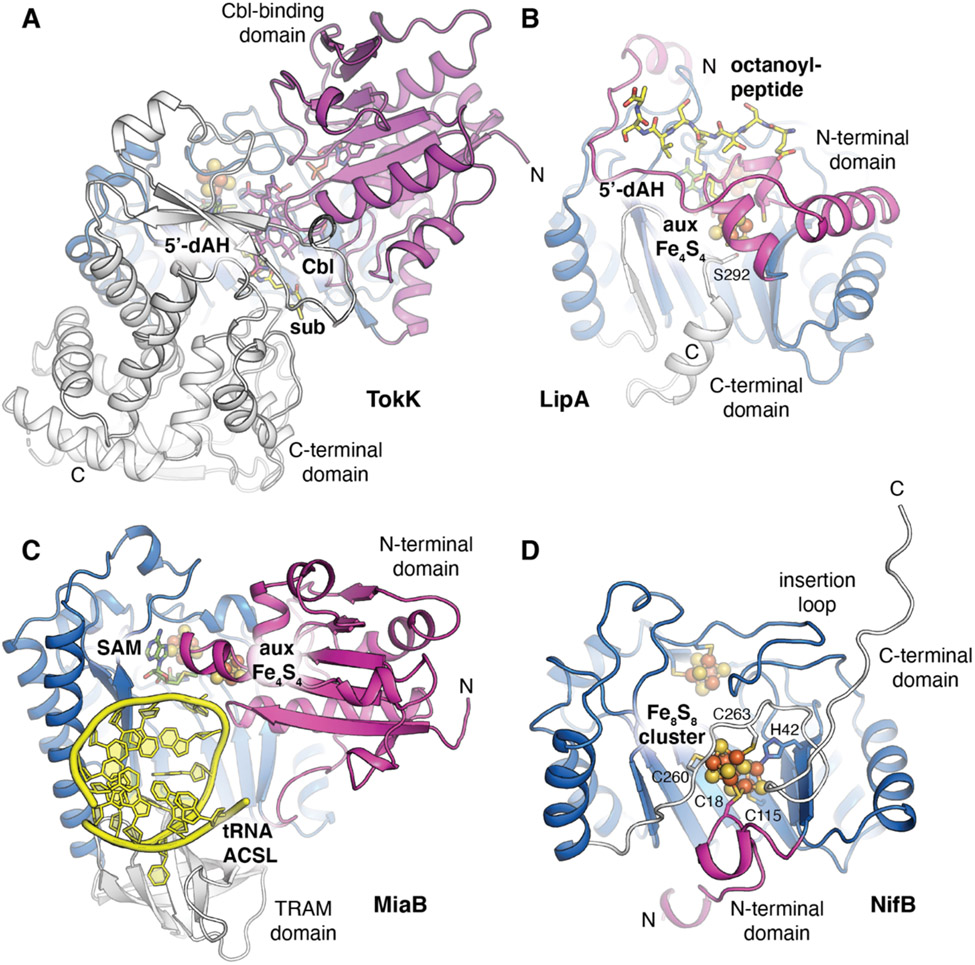
Figure 2.
A comparison of the domain architectures of radical SAM enzymes with auxiliary metallocofactors. The enzymes are colored by domain with the radical SAM core fold shown in blue. Substrates are shown as yellow sticks and cosubstrate SAM or its cleavage product (5′-dAH) are shown as green sticks. (A) Cobalamin-(Cbl)-dependent radical SAM enzyme, TokK, involved in carbapenem (sub) methylation (PDB ID 7KDY). (B) Lipoyl synthase, LipA, involved in sulfur insertion into a protein-linked fatty acid substrate (PDB ID 5EXK). (C) RNA modification enzyme, MiaB, implicated in methylthiolation of an adenine base in the anticodon stem loop (ACSL) of tRNA (PDB ID 7MJV). (D) Nitrogenase cofactor biosynthesis enzyme, NifB, involved in carbide and sulfur insertion to generate the Fe8S9C NifB-co product (PDB ID 7BI7). Selected amino acids are shown in stick format.