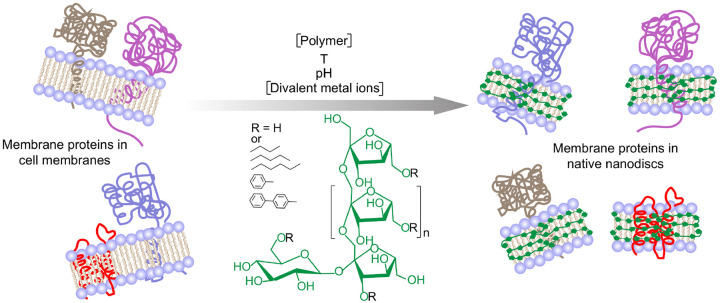
Figure 1.
Schematic of the solubilization of cell membranes using a synthetic inulin-based polymer under different solubilizations conditions, including the concentrations of the polymer and divalent metal ions (such as Ca2+ and Mg2+), temperature and pH. Reconstitution of membrane-bound proteins and other membrane components directly isolated from the cell membrane in polymer nanodiscs shown on the right. Five different synthetic non-ionic inulin-based polymers that differ in the functionalization of the hydrophobic group (R: butyl, pentyl, hexyl, phenyl, biphenyl) were used in this study. The polymer structure/polymer-belt are shown in green. Only the membrane protein-containing nanodiscs are shown, and other insoluble membrane components are omitted for clarity (right).