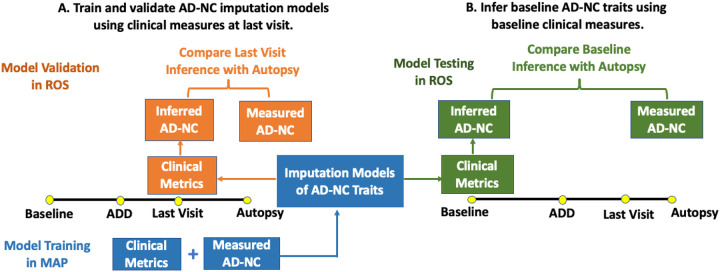
Fig 1. Overall study design to develop and validate imputation models that infer AD-NC traits based on clinical measures in older adults.
A multi-stage analytic approach was employed to develop, validate, and demonstrate the effectiveness of inferred levels of four AD-NC traits derived from clinical measures as AD biomarkers. A. We trained imputation models for four AD-NC traits using clinical data obtained at the last visit before death in MAP decedents that underwent autopsy (Fig 2). Then we validated these models in an independent cohort study (ROS) that collected the same clinical and postmortem measures. B. We tested the effectiveness as AD biomarkers for the inferred levels of four AD-NC traits at baseline, which were obtained by applying the validated imputation models to clinical measures obtained at study entry. We examined if the inferred baseline AD-NC traits predicted incident ADD (Fig 3) and discriminated adults at risk for postmortem (on average 8 years after baseline) pathologic AD in ROS cohort (Fig 4).