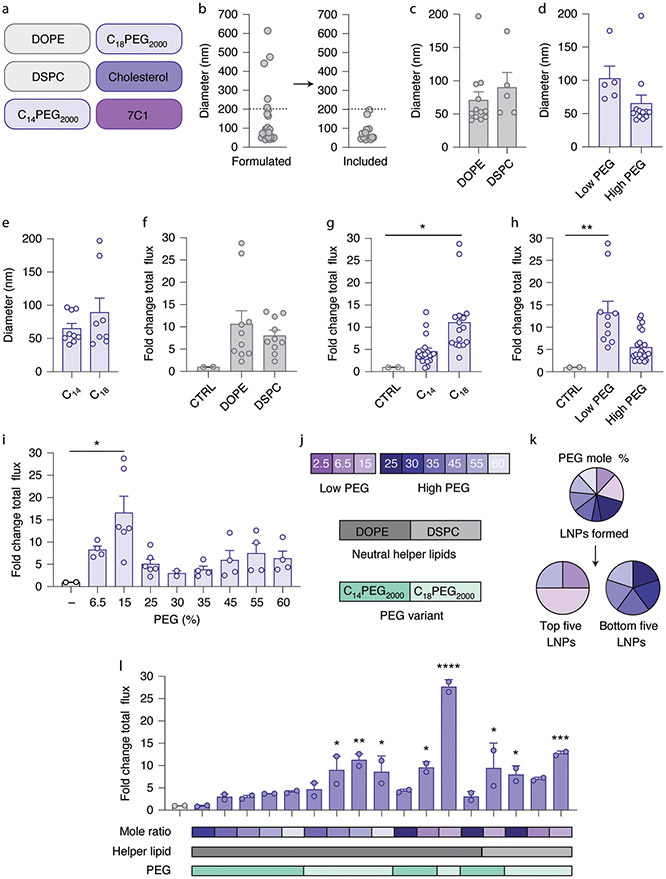
Fig. 4 ∣. A screen of LNPs containing neutral lipids from an expanded chemical space.
a, LNPs were formulated with one of two neutral lipids, one of two distinct PEG-lipids, cholesterol and the compound 7C1. b, LNPs with hydrodynamic diameter less than 200 nm as measured by DLS were tested individually in mice. c–e, LNP diameter as a function of helper lipid (c), PEG molarity (d) and PEG-lipid tail length (e). f–i, Luminescence of lungs isolated from mice relative to an untreated control 48 h after administration, plotted as a function of neutral helper lipid (f), PEG-lipid tail length (g) and PEG molarity, defined as either high and low (h) or by mole percent (i). *P = 0.024 (g), **P = 0.0089 (h), *P = 0.020 (i), one-way ANOVA, average ± s.e.m. LNPs with neutral lipids, coupled with low PEG molarity, delivered more mRNA to lungs than LNPs with high PEG molarity. j–l, PEG molarity used in this study (j), the PEG molarity found in the best- and worst-performing LNPs (k), and lung luminescence (l). For l, unless specified otherwise, ****P < 0.0001, ***P = 0.0005, **P = 0.002, *P = 0.018, *P = 0.027, *P = 0.010, *P = 0.012, *P = 0.048 (*P values arranged from left to right of l), one-way ANOVA, average ± s.e.m., n = 2 mice per group, biological replicates shown.