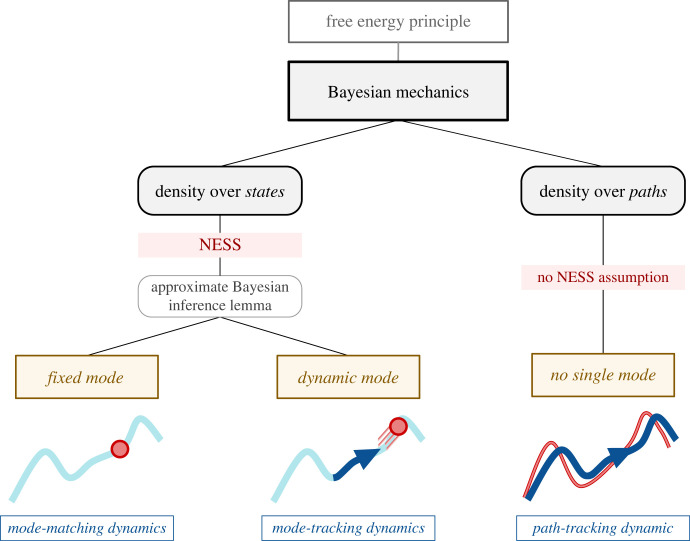
Figure 2.
Three faces of Bayesian mechanics. Under the FEP, we can define specific mechanical theories for beliefs, which defines what kinds of self-evidencing are possible in a given regime of mathematical systems. The literature contains three main applications of Bayesian mechanics, which we represent as a tree with two branching points. On the one hand, the FEP has been applied to densities over paths or trajectories of a particular system (the paths-based formulation of FEP, leading to what we call path-tracking dynamics) and to densities over states (the density dynamics formulation), which depend on a NESS solution to the mechanics of the system. The density dynamics formulation, in turn, applies to systems with a static mode, and to systems with a dynamic mode; we call the former mode-matching, and the latter mode-tracking.