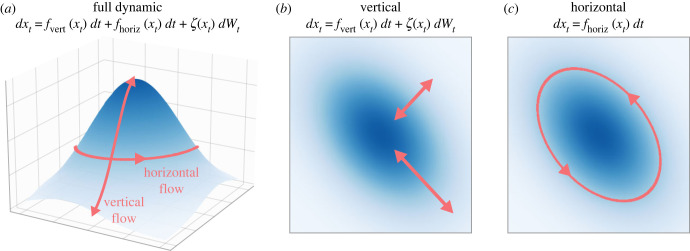
Figure 3.
Helmholtz decomposition. Splitting of flows referred to as the Helmholtz decomposition. The vertical direction consists of a gradient ascent given by and random fluctuations pushing the system away from a mode (preventing the system from collapsing to a point). The horizontal flow is a solenoidal, energetically conservative but temporally directed flow, given by a matrix operator Q.