Fig. 3.
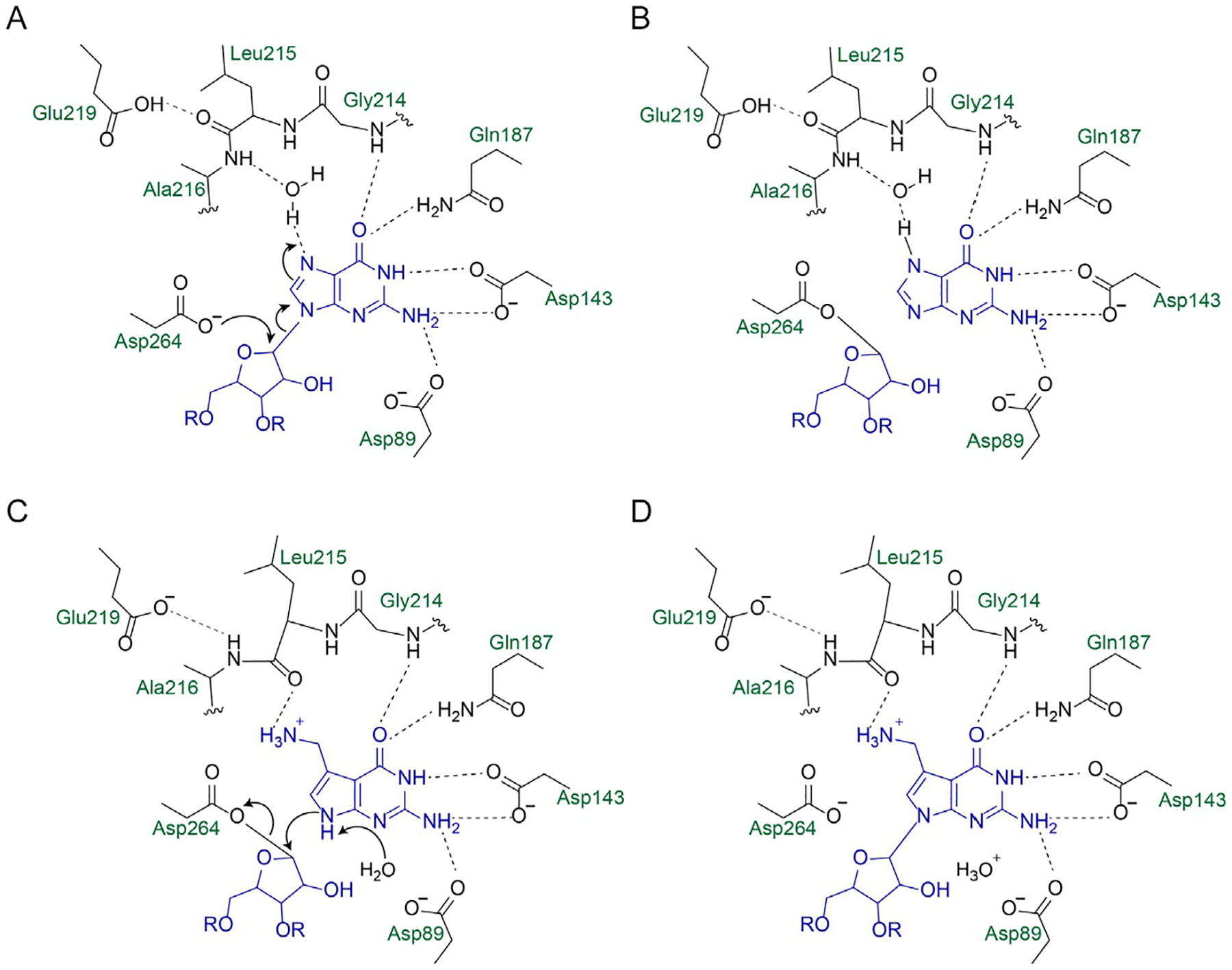
Catalytic mechanism and binding interactions of bacterial TGT with guanine and preQ1. E. coli numbering is used. (A) Asp264 acts as a nucleophile to attack the anomeric carbon of ribose 34, breaking the N–C glycosidic linkage. (B) A covalent TGT-RNA covalent intermediate is formed. (C) preQ1 replaces guanine in the binding pocket, assisted by a conformational change of the Leu215/Ala216 peptide bond. (D) N9 of preQ1 acts as a nucleophile to reform a glycosidic bond with ribose 34.
